Why Nations Fail: The Origins of Power, Prosperity, and Poverty - Daron Acemoğlu, James A. Robinson (2012)
Chapter 4. SMALL DIFFERENCES AND CRITICAL JUNCTURES: THE WEIGHT OF HISTORY
THE WORLD THE PLAGUE CREATED
IN 1346 THE BUBONIC plague, the Black Death, reached the port city of Tana at the mouth of the River Don on the Black Sea. Transmitted by fleas living on rats, the plague was brought from China by traders traveling along the Silk Road, the great trans-Asian commercial artery. Thanks to Genoese traders, the rats were soon spreading the fleas and the plague from Tana to the entire Mediterranean. By early 1347, the plague had reached Constantinople. In the spring of 1348, it was spreading through France and North Africa and up the boot of Italy. The plague wiped out about half of the population of any area it hit. Its arrival in the Italian city of Florence was witnessed firsthand by the Italian writer Giovanni Boccaccio. He later recalled:
In the face of its onrush, all the wisdom and ingenuity of man were unavailing … the plague began, in a terrifying and extraordinary manner, to make its disastrous effects apparent. It did not take the form it had assumed in the East, where if anyone bled from the nose it was an obvious portent of certain death. On the contrary, its earliest symptom was the appearance of certain swellings in the groin or armpit, some of which were egg-shaped whilst others were roughly the size of a common apple … Later on the symptoms of the disease changed, and many people began to find dark blotches and bruises on their arms, thighs and other parts of their bodies … Against these maladies … All the advice of physicians and all the power of medicine were profitless and unavailing … And in most cases death occurred within three days from the appearance of the symptoms we have described.
People in England knew the plague was coming their way and were well aware of impending doom. In mid-August 1348, King Edward III asked the Archbishop of Canterbury to organize prayers, and many bishops wrote letters for priests to read out in church to help people cope with what was about to hit them. Ralph of Shrewsbury, Bishop of Bath, wrote to his priests:
Almighty God uses thunder, lightening [sic], and other blows which issue from his throne to scourge the sons whom he wishes to redeem. Accordingly, since a catastrophic pestilence from the East has arrived in a neighboring kingdom, it is to be very much feared that, unless we pray devoutly and incessantly, a similar pestilence will stretch its poisonous branches into this realm, and strike down and consume the inhabitants. Therefore we must all come before the presence of the Lord in confession, reciting psalms.
It didn’t do any good. The plague hit and quickly wiped out about half the English population. Such catastrophes can have a huge effect on the institutions of society. Perhaps understandably, scores of people went mad. Boccaccio noted that “some maintained that an infallible way of warding off this appalling evil was to drink heavily, enjoy life to the full, go round singing and merrymaking, gratify all one’s cravings whenever the opportunity offered, and shrug the thing off as an enormous joke … and this explains why those women who recovered were possibly less chaste in the period that followed.” Yet the plague also had a socially, economically, and politically transformative impact on medieval European societies.
At the turn of the fourteenth century, Europe had a feudal order, an organization of society that first emerged in Western Europe after the collapse of the Roman Empire. It was based on a hierarchical relationship between the king and the lords beneath him, with the peasants at the bottom. The king owned the land and he granted it to the lords in exchange for military services. The lords then allocated land to peasants, in exchange for which peasants had to perform extensive unpaid labor and were subject to many fines and taxes. Peasants, who because of their “servile” status were thus called serfs, were tied to the land, unable to move elsewhere without the permission of their lord, who was not just the landlord, but also the judge, jury, and police force. It was a highly extractive system, with wealth flowing upward from the many peasants to the few lords.
The massive scarcity of labor created by the plague shook the foundations of the feudal order. It encouraged peasants to demand that things change. At Eynsham Abbey, for example, the peasants demanded that many of the fines and unpaid labor be reduced. They got what they wanted, and their new contract began with the assertion “At the time of the mortality or pestilence, which occurred in 1349, scarcely two tenants remained in the manor, and they expressed their intention of leaving unless Brother Nicholas of Upton, then abbot and lord of the manor, made a new agreement with them.” He did.
What happened at Eynsham happened everywhere. Peasants started to free themselves from compulsory labor services and many obligations to their lords. Wages started to rise. The government tried to put a stop to this and, in 1351, passed the Statute of Laborers, which commenced:
Because a great part of the people and especially of the workmen and servants has now died in that pestilence, some, seeing the straights of the masters and the scarcity of servants, are not willing to serve unless they receive excessive wages … We, considering the grave inconveniences which might come from the lack especially of ploughmen and such labourers, have … seen fit to ordain: that every man and woman of our kingdom of England … shall be bound to serve him who has seen fit so to seek after him; and he shall take only the wages liveries, meed or salary which, in the places where he sought to serve, were accustomed to be paid in the twentieth year of our reign of England [King Edward III came to the throne on January 25, 1327, so the reference here is to 1347] or the five or six common years next preceding.
The statute in effect tried to fix wages at the levels paid before the Black Death. Particularly concerning for the English elite was “enticement,” the attempt by one lord to attract the scarce peasants of another. The solution was to make prison the punishment for leaving employment without permission of the employer:
And if a reaper or mower, or other workman or servant, of whatever standing or condition he be, who is retained in the service of any one, do depart from the said service before the end of the term agreed, without permission or reasonable cause, he shall undergo the penalty of imprisonment, and let no one … moreover, pay or permit to be paid to any one more wages, livery, meed or salary than was customary as has been said.
The attempt by the English state to stop the changes of institutions and wages that came in the wake of the Black Death didn’t work. In 1381 the Peasants’ Revolt broke out, and the rebels, under the leadership of Wat Tyler, even captured most of London. Though they were ultimately defeated, and Tyler was executed, there were no more attempts to enforce the Statute of Laborers. Feudal labor services dwindled away, an inclusive labor market began to emerge in England, and wages rose.
The plague seems to have hit most of the world, and everywhere a similar fraction of the population perished. Thus the demographic impact in Eastern Europe was the same as in England and Western Europe. The social and economic forces at play were also the same. Labor was scarce and people demanded greater freedoms. But in the East, a more powerful contradictory logic was at work. Fewer people meant higher wages in an inclusive labor market. But this gave lords a greater incentive to keep the labor market extractive and the peasants servile. In England this motivation had been in play, too, as reflected in the Statute of Laborers. But workers had sufficient power that they got their way. Not so in Eastern Europe. After the plague, Eastern landlords started to take over large tracts of land and expand their holdings, which were already larger than those in Western Europe. Towns were weaker and less populous, and rather than becoming freer, workers began to see their already existing freedoms encroached on.
The effects became especially clear after 1500, when Western Europe began to demand the agricultural goods, such as wheat, rye, and livestock, produced in the East. Eighty percent of the imports of rye into Amsterdam came from the Elbe, Vistula, and Oder river valleys. Soon half of the Netherlands’ booming trade was with Eastern Europe. As Western demand expanded, Eastern landlords ratcheted up their control over the labor force to expand their supply. It was to be called the Second Serfdom, distinct and more intense than its original form of the early Middle Ages. Lords increased the taxes they levied on their tenants’ own plots and took half of the gross output. In Korczyn, Poland, all work for the lord in 1533 was paid. But by 1600 nearly half was unpaid forced labor. In 1500, workers in Mecklenberg, in eastern Germany, owed only a few days’ unpaid labor services a year. By 1550 it was one day a week, and by 1600, three days per week. Workers’ children had to work for the lord for free for several years. In Hungary, landlords took complete control of the land in 1514, legislating one day a week of unpaid labor services for each worker. In 1550 this was raised to two days per week. By the end of the century, it was three days. Serfs subject to these rules made up 90 percent of the rural population by this time.
Though in 1346 there were few differences between Western and Eastern Europe in terms of political and economic institutions, by 1600 they were worlds apart. In the West, workers were free of feudal dues, fines, and regulations and were becoming a key part of a booming market economy. In the East, they were also involved in such an economy, but as coerced serfs growing the food and agricultural goods demanded in the West. It was a market economy, but not an inclusive one. This institutional divergence was the result of a situation where the differences between these areas initially seemed very small: in the East, lords were a little better organized; they had slightly more rights and more consolidated landholdings. Towns were weaker and smaller, peasants less organized. In the grand scheme of history, these were small differences. Yet these small differences between the East and the West became very consequential for the lives of their populations and for the future path of institutional development when the feudal order was shaken up by the Black Death.
The Black Death is a vivid example of a critical juncture, a major event or confluence of factors disrupting the existing economic or political balance in society. A critical juncture is a double-edged sword that can cause a sharp turn in the trajectory of a nation. On the one hand it can open the way for breaking the cycle of extractive institutions and enable more inclusive ones to emerge, as in England. Or it can intensify the emergence of extractive institutions, as was the case with the Second Serfdom in Eastern Europe.
Understanding how history and critical junctures shape the path of economic and political institutions enables us to have a more complete theory of the origins of differences in poverty and prosperity. In addition, it enables us to account for the lay of the land today and why some nations make the transition to inclusive economic and political institutions while others do not.
THE MAKING OF INCLUSIVE INSTITUTIONS
England was unique among nations when it made the breakthrough to sustained economic growth in the seventeenth century. Major economic changes were preceded by a political revolution that brought a distinct set of economic and political institutions, much more inclusive than those of any previous society. These institutions would have profound implications not only for economic incentives and prosperity, but also for who would reap the benefits of prosperity. They were based not on consensus but, rather, were the result of intense conflict as different groups competed for power, contesting the authority of others and attempting to structure institutions in their own favor. The culmination of the institutional struggles of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries were two landmark events: the English Civil War between 1642 and 1651, and particularly the Glorious Revolution of 1688.
The Glorious Revolution limited the power of the king and the executive, and relocated to Parliament the power to determine economic institutions. At the same time, it opened up the political system to a broad cross section of society, who were able to exert considerable influence over the way the state functioned. The Glorious Revolution was the foundation for creating a pluralistic society, and it built on and accelerated a process of political centralization. It created the world’s first set of inclusive political institutions.
As a consequence, economic institutions also started becoming more inclusive. Neither slavery nor the severe economic restrictions of the feudal medieval period, such as serfdom, existed in England at the beginning of the seventeenth century. Nevertheless, there were many restrictions on economic activities people could engage in. Both the domestic and international economy were choked by monopolies. The state engaged in arbitrary taxation and manipulated the legal system. Most land was caught in archaic forms of property rights that made it impossible to sell and risky to invest in.
This changed after the Glorious Revolution. The government adopted a set of economic institutions that provided incentives for investment, trade, and innovation. It steadfastly enforced property rights, including patents granting property rights for ideas, thereby providing a major stimulus to innovation. It protected law and order. Historically unprecedented was the application of English law to all citizens. Arbitrary taxation ceased, and monopolies were abolished almost completely. The English state aggressively promoted mercantile activities and worked to promote domestic industry, not only by removing barriers to the expansion of industrial activity but also by lending the full power of the English navy to defend mercantile interests. By rationalizing property rights, it facilitated the construction of infrastructure, particularly roads, canals, and later railways, that would prove to be crucial for industrial growth.
These foundations decisively changed incentives for people and impelled the engines of prosperity, paving the way for the Industrial Revolution. First and foremost, the Industrial Revolution depended on major technological advances exploiting the knowledge base that had accumulated in Europe during the past centuries. It was a radical break from the past, made possible by scientific inquiry and the talents of a number of unique individuals. The full force of this revolution came from the market that created profitable opportunities for technologies to be developed and applied. It was the inclusive nature of markets that allowed people to allocate their talents to the right lines of business. It also relied on education and skills, for it was the relatively high levels of education, at least by the standards of the time, that enabled the emergence of entrepreneurs with the vision to employ new technologies for their businesses and to find workers with the skills to use them.
It is not a coincidence that the Industrial Revolution started in England a few decades following the Glorious Revolution. The great inventors such as James Watt (perfecter of the steam engine), Richard Trevithick (the builder of the first steam locomotive), Richard Arkwright (the inventor of the spinning frame), and Isambard Kingdom Brunel (the creator of several revolutionary steamships) were able to take up the economic opportunities generated by their ideas, were confident that their property rights would be respected, and had access to markets where their innovations could be profitably sold and used. In 1775, just after he had the patent renewed on his steam engine, which he called his “Fire engine,” James Watt wrote to his father:
Dear Father,
After a series of various and violent Oppositions I have at last got an Act of Parliament vesting the property of my new Fire engines in me and my Assigns, throughout Great Britain & the plantations for twenty five years to come, which I hope will be very beneficial to me, as there is already considerable demand for them.
This letter reveals two things. First, Watt was motivated by the market opportunities he anticipated, by the “considerable demand” in Great Britain and its plantations, the English overseas colonies. Second, it shows how he was able to influence Parliament to get what he wanted since it was responsive to the appeals of individuals and innovators.
The technological advances, the drive of businesses to expand and invest, and the efficient use of skills and talent were all made possible by the inclusive economic institutions that England developed. These in turn were founded on her inclusive political institutions.
England developed these inclusive political institutions because of two factors. First were political institutions, including a centralized state, that enabled her to take the next radical—in fact, unprecedented—step toward inclusive institutions with the onset of the Glorious Revolution. While this factor distinguished England from much of the world, it did not significantly differentiate it from Western European countries such as France and Spain. More important was the second factor. The events leading up to the Glorious Revolution forged a broad and powerful coalition able to place durable constraints on the power of the monarchy and the executive, which were forced to be open to the demands of this coalition. This laid the foundations for pluralistic political institutions, which then enabled the development of economic institutions that would underpin the first Industrial Revolution.
SMALL DIFFERENCES THAT MATTER
World inequality dramatically increased with the British, or English, Industrial Revolution because only some parts of the world adopted the innovations and new technologies that men such as Arkwright and Watt, and the many who followed, developed. The response of different nations to this wave of technologies, which determined whether they would languish in poverty or achieve sustained economic growth, was largely shaped by the different historical paths of their institutions. By the middle of the eighteenth century, there were already notable differences in political and economic institutions around the world. But where did these differences come from?
English political institutions were on their way to much greater pluralism by 1688, compared with those in France and Spain, but if we go back in time one hundred years, to 1588, the differences shrink to almost nothing. All three countries were ruled by relatively absolutist monarchs: Elizabeth I in England, Philip II in Spain, and Henry II in France. All were battling with assemblies of citizens—such as the Parliament in England, the Cortes in Spain, and the Estates-General in France—that were demanding more rights and control over the monarchy. These assemblies all had somewhat different powers and scopes. For instance, the English Parliament and the Spanish Cortes had power over taxation, while the Estates-General did not. In Spain this mattered little, because after 1492 the Spanish Crown had a vast American empire and benefited massively from the gold and silver found there. In England the situation was different. Elizabeth I was far less financially independent, so she had to beg Parliament for more taxes. In exchange, Parliament demanded concessions, in particular restrictions on the right of Elizabeth to create monopolies. It was a conflict Parliament gradually won. In Spain the Cortes lost a similar conflict. Trade wasn’t just monopolized; it was monopolized by the Spanish monarchy.
These distinctions, which initially appeared small, started to matter a great deal in the seventeenth century. Though the Americas had been discovered by 1492 and Vasco da Gama had reached India by rounding the Cape of Good Hope, at the southern tip of Africa, in 1498, it was only after 1600 that a huge expansion of world trade, particularly in the Atlantic, started to take place. In 1585 the first English colonization of North America began at Roanoke, in what is now North Carolina. In 1600 the English East India Company was formed. In 1602 it was followed by the Dutch equivalent. In 1607 the colony of Jamestown was founded by the Virginia Company. By the 1620s the Caribbean was being colonized, with Barbados occupied in 1627. France was also expanding in the Atlantic, founding Quebec City in 1608 as the capital of New France in what is now Canada. The consequences of this economic expansion for institutions were very different for England than for Spain and France because of small initial differences.
Elizabeth I and her successors could not monopolize the trade with the Americas. Other European monarchs could. So while in England, Atlantic trade and colonization started creating a large group of wealthy traders with few links to the Crown, this was not the case in Spain or France. The English traders resented royal control and demanded changes in political institutions and the restriction of royal prerogatives. They played a critical role in the English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution. Similar conflicts took place everywhere. French kings, for example, faced the Fronde Rebellion between 1648 and 1652. The difference was that in England it was far more likely that the opponents to absolutism would prevail because they were relatively wealthy and more numerous than the opponents to absolutism in Spain and France.
The divergent paths of English, French, and Spanish societies in the seventeenth century illustrate the importance of the interplay of small institutional differences with critical junctures. During critical junctures, a major event or confluence of factors disrupts the existing balance of political or economic power in a nation. These can affect only a single country, such as the death of Chairman Mao Zedong in 1976, which at first created a critical juncture only for Communist China. Often, however, critical junctures affect a whole set of societies, in the way that, for example, colonization and then decolonization affected most of the globe.
Such critical junctures are important because there are formidable barriers against gradual improvements, resulting from the synergy between extractive political and economic institutions and the support they give each other. The persistence of this feedback loop creates a vicious circle. Those who benefit from the status quo are wealthy and well organized, and can effectively fight major changes that will take away their economic privileges and political power.
Once a critical juncture happens, the small differences that matter are the initial institutional differences that put in motion very different responses. This is the reason why the relatively small institutional differences in England, France, and Spain led to fundamentally different development paths. The paths resulted from the critical juncture created by the economic opportunities presented to Europeans by Atlantic trade.
Even if small institutional differences matter greatly during critical junctures, not all institutional differences are small, and naturally, larger institutional differences lead to even more divergent patterns during such junctures. While the institutional differences between England and France were small in 1588, the differences between Western and Eastern Europe were much greater. In the West, strong centralized states such as England, France, and Spain had latent constitutional institutions (Parliament, the Estates-General, and the Cortes). There were also underlying similarities in economic institutions, such as the lack of serfdom.
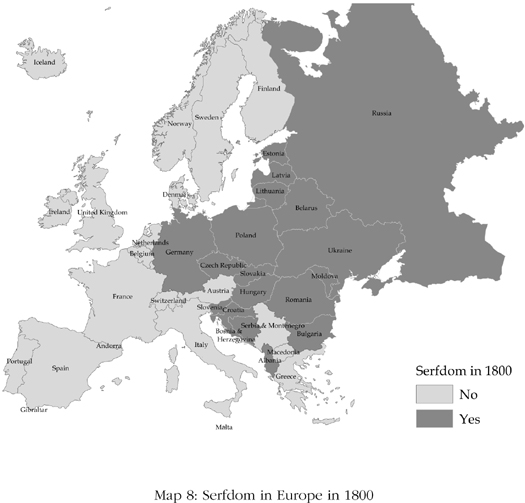
Eastern Europe was a different matter. The kingdom of Poland-Lithuania, for example, was ruled by an elite class called the Szlachta, who were so powerful they had even introduced elections for kings. This was not absolute rule as in France under Louis XIV, the Sun King, but absolutism of an elite, extractive political institutions all the same. The Szlachta ruled over a mostly rural society dominated by serfs, who had no freedom of movement or economic opportunities. Farther east, the Russian emperor Peter the Great was also consolidating an absolutism far more intense and extractive than even Louis XIV could manage. Map 8 provides one simple way of seeing the extent of the divergence between Western and Eastern Europe at the beginning of the nineteenth century. It plots whether or not a country still had serfdom in 1800. Countries that appear dark did; those that are light did not. Eastern Europe is dark; Western Europe is light.
Yet the institutions of Western Europe had not always been so different from those in the East. They began, as we saw earlier, to diverge in the fourteenth century when the Black Death hit in 1346. There were small differences between political and economic institutions in Western and Eastern Europe. England and Hungary were even ruled by members of the same family, the Angevins. The more important institutional differences that emerged after the Black Death then created the background upon which the more significant divergence between the East and the West would play out during the seventeenth, eighteenth, and nineteenth centuries.
But where do the small institutional differences that start this process of divergence arise in the first place? Why did Eastern Europe have different political and economic institutions than the West in the fourteenth century? Why was the balance of power between Crown and Parliament different in England than in France and Spain? As we will see in the next chapter, even societies that are far less complex than our modern society create political and economic institutions that have powerful effects on the lives of their members. This is true even for hunter-gatherers, as we know from surviving societies such as the San people of modern Botswana, who do not farm or even live in permanent settlements.
No two societies create the same institutions; they will have distinct customs, different systems of property rights, and different ways of dividing a killed animal or loot stolen from another group. Some will recognize the authority of elders, others will not; some will achieve some degree of political centralization early on, but not others. Societies are constantly subject to economic and political conflict that is resolved in different ways because of specific historical differences, the role of individuals, or just random factors.
These differences are often small to start with, but they cumulate, creating a process of institutional drift. Just as two isolated populations of organisms will drift apart slowly in a process of genetic drift, because random genetic mutations cumulate, two otherwise similar societies will also slowly drift apart institutionally. Though, just like genetic drift, institutional drift has no predetermined path and does not even need to be cumulative; over centuries it can lead to perceptible, sometimes important differences. The differences created by institutional drift become especially consequential, because they influence how society reacts to changes in economic or political circumstances during critical junctures.
The richly divergent patterns of economic development around the world hinge on the interplay of critical junctures and institutional drift. Existing political and economic institutions—sometimes shaped by a long process of institutional drift and sometimes resulting from divergent responses to prior critical junctures—create the anvil upon which future change will be forged. The Black Death and the expansion of world trade after 1600 were both major critical junctures for European powers and interacted with different initial institutions to create a major divergence. Because in 1346 in Western Europe peasants had more power and autonomy than they did in Eastern Europe, the Black Death led to the dissolution of feudalism in the West and the Second Serfdom in the East. Because Eastern and Western Europe had started to diverge in the fourteenth century, the new economic opportunities of the seventeenth, eighteenth, and nineteenth centuries would also have fundamentally different implications for these different parts of Europe. Because in 1600 the grip of the Crown was weaker in England than in France and Spain, Atlantic trade opened the way to the creation of new institutions with greater pluralism in England, while strengthening the French and Spanish monarchs.
THE CONTINGENT PATH OF HISTORY
The outcomes of the events during critical junctures are shaped by the weight of history, as existing economic and political institutions shape the balance of power and delineate what is politically feasible. The outcome, however, is not historically predetermined but contingent. The exact path of institutional development during these periods depends on which one of the opposing forces will succeed, which groups will be able to form effective coalitions, and which leaders will be able to structure events to their advantage.
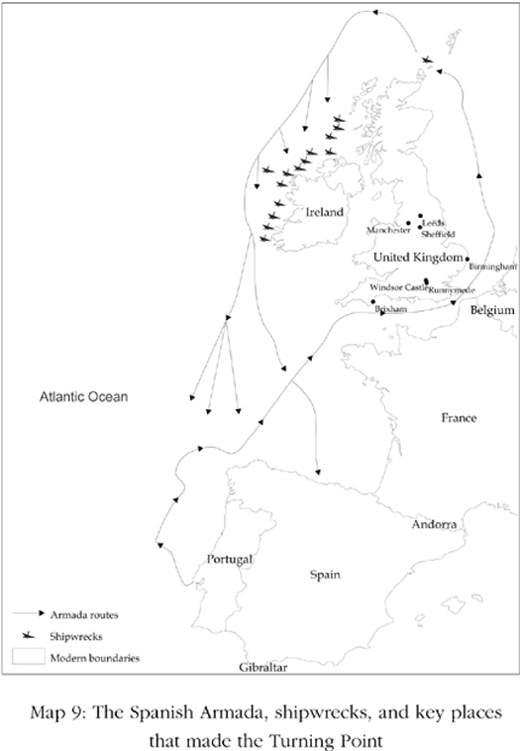
The role of contingency can be illustrated by the origins of inclusive political institutions in England. Not only was there nothing preordained in the victory of the groups vying for limiting the power of the Crown and for more pluralistic institutions in the Glorious Revolution of 1688, but the entire path leading up to this political revolution was at the mercy of contingent events. The victory of the winning groups was inexorably linked to the critical juncture created by the rise of Atlantic trade that enriched and emboldened merchants opposing the Crown. But a century earlier it was far from obvious that England would have any ability to dominate the seas, colonize many parts of the Caribbean and North America, or capture so much of the lucrative trade with the Americas and the East. Neither Elizabeth I nor other Tudor monarchs before her had built a powerful, unified navy. The English navy relied on privateers and independent merchant ships and was much less powerful than the Spanish fleet. The profits of the Atlantic nonetheless attracted these privateers, challenging the Spanish monopoly of the ocean. In 1588 the Spanish decided to put an end to these challenges to their monopoly, as well as to English meddling in the Spanish Netherlands, at the time fighting against Spain for independence.
The Spanish monarch Philip II sent a powerful fleet, the Armada, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia. It appeared a foregone conclusion to many that the Spanish would conclusively defeat the English, solidify their monopoly of the Atlantic, and probably overthrow Elizabeth I, perhaps ultimately gaining control of the British Isles. Yet something very different transpired. Bad weather and strategic mistakes by Sidonia, who had been put in charge at the last minute after a more experienced commander died, made the Spanish Armada lose their advantage. Against all odds, the English destroyed much of the fleet of their more powerful opponents. The Atlantic seas were now open to the English on more equal terms. Without this unlikely victory for the English, the events that would create the transformative critical juncture and spawn the distinctively pluralistic political institutions of post-1688 England would never have got moving. Map 9 shows the trail of Spanish shipwrecks as the Armada was chased right around the British Isles.
Of course, nobody in 1588 could foresee the consequences of the fortunate English victory. Few probably understood at the time that this would create a critical juncture leading up to a major political revolution a century later.
There should be no presumption that any critical juncture will lead to a successful political revolution or to change for the better. History is full of examples of revolutions and radical movements replacing one tyranny with another, in a pattern that the German sociologist Robert Michels dubbed the iron law of oligarchy, a particularly pernicious form of the vicious circle. The end of colonialism in the decades following the Second World War created critical junctures for many former colonies. However, in most cases in sub-Saharan Africa and many in Asia, the postindependence governments simply took a page out of Robert Michels’s book and repeated and intensified the abuses of their predecessors, often severely narrowing the distribution of political power, dismantling constraints, and undermining the already meager incentives that economic institutions provided for investment and economic progress. It was only in a few cases, societies such as Botswana (see this page), that critical junctures were used to launch a process of political and economic change that paved the way for economic growth.
Critical junctures can also result in major change toward rather than away from extractive institutions. Inclusive institutions, even though they have their own feedback loop, the virtuous circle, can also reverse course and become gradually more extractive because of challenges during critical junctures—and whether this happens is, again, contingent. The Venetian Republic, as we will see in chapter 6, made major strides toward inclusive political and economic institutions in the medieval period. But while such institutions became gradually stronger in England after the Glorious Revolution of 1688, in Venice they ultimately transformed themselves into extractive institutions under the control of a narrow elite that monopolized both economic opportunities and political power.
UNDERSTANDING THE LAY OF THE LAND
The emergence of a market economy based on inclusive institutions and sustained economic growth in eighteenth-century England sent ripples all around the world, not least because it allowed England to colonize a large part of it. But if the influence of English economic growth certainly spread around the globe, the economic and political institutions that created it did not automatically do so. The diffusion of the Industrial Revolution had different effects on the world in the same way that the Black Death had different effects on Western and Eastern Europe, and in the same way that the expansion of Atlantic trade had different effects in England and Spain. It was the institutions in place in different parts of the world that determined the impact, and these institutions were indeed different—small differences had been amplified over time by prior critical junctures. These institutional differences and their implications have tended to persist to the present due to the vicious and virtuous circles, albeit imperfectly, and are the key to understanding both how world inequality emerged and the nature of the lay of the land around us.
Some parts of the world developed institutions that were very close to those in England, though by a very different route. This was particularly true of some European “settler colonies” such as Australia, Canada, and the United States, though their institutions were just forming as the Industrial Revolution was getting under way. As we saw in chapter 1, a process starting with the foundation of the Jamestown colony in 1607 and culminating in the War of Independence and the enactment of the U.S. Constitution shares many of the same characteristics as the long struggle in England of Parliament against the monarchy, for it also led to a centralized state with pluralistic political institutions. The Industrial Revolution then spread rapidly to such countries.
Western Europe, experiencing many of the same historical processes, had institutions similar to England at the time of the Industrial Revolution. There were small but consequential differences between England and the rest, which is why the Industrial Revolution happened in England and not France. This revolution then created an entirely new situation and considerably different sets of challenges to European regimes, which in turn spawned a new set of conflicts culminating in the French Revolution. The French Revolution was another critical juncture that led the institutions of Western Europe to converge with those of England, while Eastern Europe diverged further.
The rest of the world followed different institutional trajectories. European colonization set the stage for institutional divergence in the Americas, where in contrast to the inclusive institutions developed in the United States and Canada extractive ones emerged in Latin America, which explains the patterns of inequality we see in the Americas. The extractive political and economic institutions of the Spanish conquistadors in Latin America have endured, condemning much of the region to poverty. Argentina and Chile have, however, fared better than most other countries in the region. They had few indigenous people or mineral riches and were “neglected” while the Spanish focused on the lands occupied by the Aztec, Maya, and Incan civilizations. Not coincidentally, the poorest part of Argentina is the northwest, the only section of the country integrated into the Spanish colonial economy. Its persistent poverty, the legacy of extractive institutions, is similar to that created by the Potosí mita in Bolivia and Peru (this page-this page).
Africa was the part of the world with the institutions least able to take advantage of the opportunities made available by the Industrial Revolution. For at least the last one thousand years, outside of small pockets and during limited periods of time, Africa has lagged behind the rest of the world in terms of technology, political development, and prosperity. It is the part of the world where centralized states formed very late and very tenuously. Where they did form, they were likely as highly absolutist as the Kongo and often short lived, usually collapsing. Africa shares this trajectory of lack of state centralization with countries such as Afghanistan, Haiti, and Nepal, which have also failed to impose order over their territories and create anything resembling stability to achieve even a modicum of economic progress. Though located in very different parts of the world, Afghanistan, Haiti, and Nepal have much in common institutionally with most nations in sub-Saharan Africa, and are thus some of the poorest countries in the world today.
How African institutions evolved into their present-day extractive form again illustrates the process of institutional drift punctuated by critical junctures, but this time often with highly perverse outcomes, particularly during the expansion of the Atlantic slave trade. There were new economic opportunities for the Kingdom of Kongo when European traders arrived. The long-distance trade that transformed Europe also transformed the Kingdom of Kongo, but again, initial institutional differences mattered. Kongolese absolutism transmogrified from completely dominating society, with extractive economic institutions that merely captured all the agricultural output of its citizens, to enslaving people en masse and selling them to the Portuguese in exchange for guns and luxury goods for the Kongolese elite.
The initial differences between England and Kongo meant that while new long-distance trade opportunities created a critical juncture toward pluralistic political institutions in the former, they also extinguished any hope of absolutism being defeated in the Kongo. In much of Africa the substantial profits to be had from slaving led not only to its intensification and even more insecure property rights for the people but also to intense warfare and the destruction of many existing institutions; within a few centuries, any process of state centralization was totally reversed, and many of the African states had largely collapsed. Though some new, and sometimes powerful, states did form to exploit the slave trade, they were based on warfare and plunder. The critical juncture of the discovery of the Americas may have helped England develop inclusive institutions but it made institutions in Africa even more extractive.
Though the slave trade mostly ended after 1807, subsequent European colonialism not only threw into reverse nascent economic modernization in parts of southern and western Africa but also cut off any possibility of indigenous institutional reform. This meant that even outside of areas such as Congo, Madagascar, Namibia, and Tanzania, the areas where plunder, mass disruption, and even whole-scale murder were the rule, there was little chance for Africa to change its institutional path.
Even worse, the structures of colonial rule left Africa with a more complex and pernicious institutional legacy in the 1960s than at the start of the colonial period. The development of the political and economic institutions in many African colonies meant that rather than creating a critical juncture for improvements in their institutions, independence created an opening for unscrupulous leaders to take over and intensify the extraction that European colonialists presided over. The political incentives these structures created led to a style of politics that reproduced the historical patterns of insecure and inefficient property rights under states with strong absolutist tendencies but nonetheless lacking any centralized authority over their territories.
The Industrial Revolution has still not spread to Africa because that continent has experienced a long vicious circle of the persistence and re-creation of extractive political and economic institutions. Botswana is the exception. As we will see (this page-this page), in the nineteenth century, King Khama, the grandfather of Botswana’s first prime minister at independence, Seretse Khama, initiated institutional changes to modernize the political and economic institutions of his tribe. Quite uniquely, these changes were not destroyed in the colonial period, partly as a consequence of Khama’s and other chiefs’ clever challenges to colonial authority. Their interplay with the critical juncture that independence from colonial rule created laid the foundations for Botswana’s economic and political success. It was another case of small historical differences mattering.
There is a tendency to see historical events as the inevitable consequences of deep-rooted forces. While we place great emphasis on how the history of economic and political institutions creates vicious and virtuous circles, contingency, as we have emphasized in the context of the development of English institutions, can always be a factor. Seretse Khama, studying in England in the 1940s, fell in love with Ruth Williams, a white woman. As a result, the racist apartheid regime in South Africa persuaded the English government to ban him from the protectorate, then called Bechuanaland (whose administration was under the High Commissioner of South Africa), and he resigned his kingship. When he returned to lead the anticolonial struggle, he did so with the intention not of entrenching the traditional institutions but of adapting them to the modern world. Khama was an extraordinary man, uninterested in personal wealth and dedicated to building his country. Most other African countries have not been so fortunate. Both things mattered, the historical development of institutions in Botswana and contingent factors that led these to be built on rather than overthrown or distorted as they were elsewhere in Africa.
IN THE NINETEENTH CENTURY, absolutism not so different from that in Africa or Eastern Europe was blocking the path of industrialization in much of Asia. In China, the state was strongly absolutist, and independent cities, merchants, and industrialists were either nonexistent or much weaker politically. China was a major naval power and heavily involved in long-distance trade centuries before the Europeans. But it had turned away from the oceans just at the wrong time, when Ming emperors decided in the late fourteenth and early fifteenth centuries that increased long-distance trade and the creative destruction that it might bring would be likely to threaten their rule.
In India, institutional drift worked differently and led to the development of a uniquely rigid hereditary caste system that limited the functioning of markets and the allocation of labor across occupations much more severely than the feudal order in medieval Europe. It also underpinned another strong form of absolutism under the Mughal rulers. Most European countries had similar systems in the Middle Ages. Modern Anglo-Saxon surnames such as Baker, Cooper, and Smith are direct descendants of hereditary occupational categories. Bakers baked, coopers made barrels, and smiths forged metals. But these categories were never as rigid as Indian caste distinctions and gradually became meaningless as predictors of a person’s occupation. Though Indian merchants did trade throughout the Indian Ocean, and a major textile industry developed, the caste system and Mughal absolutism were serious impediments to the development of inclusive economic institutions in India. By the nineteenth century, things were even less hospitable for industrialization as India became an extractive colony of the English. China was never formally colonized by a European power, but after the English successfully defeated the Chinese in the Opium Wars between 1839 and 1842, and then again between 1856 and 1860, China had to sign a series of humiliating treaties and allow European exports to enter. As China, India, and others failed to take advantage of commercial and industrial opportunities, Asia, except for Japan, lagged behind as Western Europe was forging ahead.
THE COURSE OF institutional development that Japan charted in the nineteenth century again illustrates the interaction between critical junctures and small differences created by institutional drift. Japan, like China, was under absolutist rule. The Tokugawa family took over in 1600 and ruled over a feudal system that also banned international trade. Japan, too, faced a critical juncture created by Western intervention as four U.S. warships, commanded by Matthew C. Perry, entered Edo Bay in July 1853, demanding trade concessions similar to those England obtained from the Chinese in the Opium Wars. But this critical juncture played out very differently in Japan. Despite their proximity and frequent interactions, by the nineteenth century China and Japan had already drifted apart institutionally.
While Tokugawa rule in Japan was absolutist and extractive, it had only a tenuous hold on the leaders of the other major feudal domains and was susceptible to challenge. Even though there were peasant rebellions and civil strife, absolutism in China was stronger, and the opposition less organized and autonomous. There were no equivalents of the leaders of the other domains in China who could challenge the absolutist rule of the emperor and trace an alternative institutional path. This institutional difference, in many ways small relative to the differences separating China and Japan from Western Europe, had decisive consequences during the critical juncture created by the forceful arrival of the English and Americans. China continued in its absolutist path after the Opium Wars, while the U.S. threat cemented the opposition to Tokugawa rule in Japan and led to a political revolution, the Meiji Restoration, as we will see in chapter 10. This Japanese political revolution enabled more inclusive political institutions and much more inclusive economic institutions to develop, and laid the foundations for subsequent rapid Japanese growth, while China languished under absolutism.
How Japan reacted to the threat posed by U.S. warships, by starting a process of fundamental institutional transformation, helps us understand another aspect of the lay of the land around us: transitions from stagnation to rapid growth. South Korea, Taiwan, and finally China achieved breakneck rates of economic growth since the Second World War through a path similar to the one that Japan took. In each of these cases, growth was preceded by historic changes in the countries’ economic institutions—though not always in their political institutions, as the Chinese case highlights.
The logic of how episodes of rapid growth come to an abrupt end and are reversed is also related. In the same way that decisive steps toward inclusive economic institutions can ignite rapid economic growth, a sharp turn away from inclusive institutions can lead to economic stagnation. But more often, collapses of rapid growth, such as in Argentina or the Soviet Union, are a consequence of growth under extractive institutions coming to an end. As we have seen, this can happen either because of infighting over the spoils of extraction, leading to the collapse of the regime, or because the inherent lack of innovation and creative destruction under extractive institutions puts a limit on sustained growth. How the Soviets ran hard into these limits will be discussed in greater detail in the next chapter.
IF THE POLITICAL and economic institutions of Latin America over the past five hundred years were shaped by Spanish colonialism, those of the Middle East were shaped by Ottoman colonialism. In 1453 the Ottomans under Sultan Mehmet II captured Constantinople, making it their capital. During the rest of the century, the Ottomans conquered large parts of the Balkans and most of the rest of Turkey. In the first half of the sixteenth century, Ottoman rule spread throughout the Middle East and North Africa. By 1566, at the death of Sultan Süleyman I, known as the Magnificent, their empire stretched from Tunisia in the East, through Egypt, all the way to Mecca in the Arabian Peninsula, and on to what is now modern Iraq. The Ottoman state was absolutist, with the sultan accountable to few and sharing power with none. The economic institutions the Ottomans imposed were highly extractive. There was no private property in land, which all formally belonged to the state. Taxation of land and agricultural output, together with loot from war, was the main source of government revenues. However, the Ottoman state did not dominate the Middle East in the same way that it could dominate its heartland in Anatolia or even to the extent that the Spanish state dominated Latin American society. The Ottoman state was continuously challenged by Bedouins and other tribal powers in the Arabian Peninsula. It lacked not only the ability to impose a stable order in much of the Middle East but also the administrative capacity to collect taxes. So it “farmed” them out to individuals, selling off the right to others to collect taxes in whatever way they could. These tax farmers became autonomous and powerful. Rates of taxation in the Middle Eastern territories were very high, varying between one-half or two-thirds of what farmers produced. Much of this revenue was kept by the tax farmers. Because the Ottoman state failed to establish a stable order in these areas, property rights were far from secure, and there was a great deal of lawlessness and banditry as armed groups vied for local control. In Palestine, for example, the situation was so dire that starting in the late sixteenth century, peasants left the most fertile land and moved up to mountainous areas, which gave them greater protection against banditry.
Extractive economic institutions in the urban areas of the Ottoman Empire were no less stifling. Commerce was under state control, and occupations were strictly regulated by guilds and monopolies. The consequence was that at the time of the Industrial Revolution the economic institutions of the Middle East were extractive. The region stagnated economically.
By the 1840s, the Ottomans were trying to reform institutions—for example, by reversing tax farming and getting locally autonomous groups under control. But absolutism persisted until the First World War, and reform efforts were thwarted by the usual fear of creative destruction and the anxiety among elite groups that they would lose economically or politically. While Ottoman reformers talked of introducing private property rights to land in order to increase agricultural productivity, the status quo persisted because of the desire for political control and taxation. Ottoman colonization was followed by European colonization after 1918. When European control ended, the same dynamics we have seen in sub-Saharan Africa took hold, with extractive colonial institutions taken over by independent elites. In some cases, such as the monarchy of Jordan, these elites were direct creations of the colonial powers, but this, too, happened frequently in Africa, as we will see. Middle Eastern countries without oil today have income levels similar to poor Latin American nations. They did not suffer from such immiserizing forces as the slave trade, and they benefited for a longer period from flows of technology from Europe. In the Middle Ages, the Middle East itself was also a relatively advanced part of the world economically. So today it is not as poor as Africa, but the majority of its people still live in poverty.
![]()
WE HAVE SEEN that neither geographic- nor cultural- nor ignorance-based theories are helpful for explaining the lay of the land around us. They do not provide a satisfactory account for the prominent patterns of world inequality: the fact that the process of economic divergence started with the Industrial Revolution in England during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries and then spread to Western Europe and to European settler colonies; the persistent divergence between different parts of the Americas; the poverty of Africa or the Middle East; the divergence between Eastern and Western Europe; and the transitions from stagnation to growth and the sometimes abrupt end to growth spurts. Our institutional theory does.
In the remaining chapters, we will discuss in greater detail how this institutional theory works and illustrate the wide range of phenomena it can account for. These range from the origins of the Neolithic Revolution to the collapse of several civilizations, either because of the intrinsic limits to growth under extractive institutions or because of limited steps toward inclusiveness being reversed.
We will see how and why decisive steps toward inclusive political institutions were taken during the Glorious Revolution in England. We will look more specifically at the following:
✵ How inclusive institutions emerged from the interplay of the critical juncture created by Atlantic trade and the nature of preexisting English institutions.
✵ How these institutions persisted and became strengthened to lay the foundations for the Industrial Revolution, thanks in part to the virtuous circle and in part to fortunate turns of contingency.
✵ How many regimes reigning over absolutist and extractive institutions steadfastly resisted the spread of new technologies unleashed by the Industrial Revolution.
✵ How Europeans themselves stamped out the possibility of economic growth in many parts of the world that they conquered.
✵ How the vicious circle and the iron law of oligarchy have created a powerful tendency for extractive institutions to persist, and thus the lands where the Industrial Revolution originally did not spread remain relatively poor.
✵ Why the Industrial Revolution and other new technologies have not spread and are unlikely to spread to places around the world today where a minimum degree of centralization of the state hasn’t been achieved.
Our discussion will also show that certain areas that managed to transform institutions in a more inclusive direction, such as France or Japan, or that prevented the establishment of extractive institutions, such as the United States or Australia, were more receptive to the spread of the Industrial Revolution and pulled ahead of the rest. As in England, this was not always a smooth process, and along the way, many challenges to inclusive institutions were overcome, sometimes because of the dynamics of the virtuous circle, sometimes thanks to the contingent path of history.
Finally, we will also discuss how the failure of nations today is heavily influenced by their institutional histories, how much policy advice is informed by incorrect hypotheses and is potentially misleading, and how nations are still able to seize critical junctures and break the mold to reform their institutions and embark upon a path to greater prosperity.