The Art of Digital Marketing: The Definitive Guide to Creating Strategic, Targeted, and Measurable Online Campaigns - Ian Dodson (2016)
Chapter 7. SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING (PART 2)
An Introduction
From a customer's point of view, social media is an awesome way to connect with people she already knows—and to connect with people or businesses she wants to know. As a digital marketer, you need to use this curiosity to drive your business without approaching customers in an obtrusive way. While social media is a playground where people can flit between discussions and encounter great deals and offers on their own terms, your job is to deliver content that your target audience wants to receive, which will be of great benefit to them—and even better benefit to you.
Implementing an effective social media strategy for your business is imperative to the success of a social media campaign, and the only way to build and sustain relationships with customers is to listen to them.
Process
Chapter 6 gave you the lowdown on the first two stages of the SMM iterative process, as shown in Figure 7.1. This chapter will keep the wheel spinning so that you will have complete knowledge of the third and fourth stages:
1. 3. Implementation. Being engaged with your customers on social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn will keep customers interested, but don't just be the best friend—be the mentor who will know what your audience wants in advance, by planning and scheduling content. In this stage you will learn how to set appropriate goals for your chosen social media platforms and to create and manage your campaigns in line with your budget and proposed timeline.
2. 4. Analysis. While some friendships come to a natural end, your social media campaign never stops turning. But as a true friendship blossoms with understanding and trust, your campaign cannot succeed without constant analysis. This stage guides you through the analysis and measurement services that each major platform offers, in order to track the effectiveness of your social media campaigns.
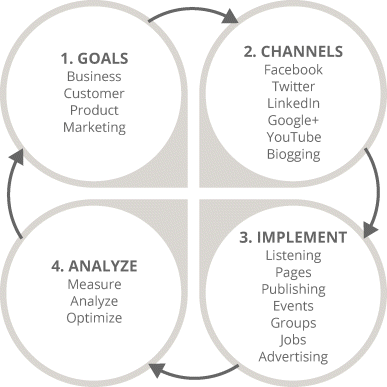
Figure 7.1 Four-Stage SMM Process
Key Terms and Concepts
This chapter will teach you to understand why implementing social media strategies will better equip you to reach achievable goals, and how you will benefit from the analysis tools that each social media platform offers. Upon completion of SMM part 2, you will:
· Master the intricacies of each social media platforms' analysis features.
· Be adept at scheduling appropriate content for each social media platform.
· Learn how to set suitable goals for your chosen social media platform.
· Create and manage your social media campaigns to budget and schedule.
· Be aware of privacy and data protection issues associated with SMM.
If Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and all of the other social media platforms were in high school, each would be a member of a completely different clique. Your role as a digital marketer is to be a social butterfly who understands what drives each network, why it works, and how to keep the members of each network engaged.
Stage 3: Implementation
You have learned the basic elements of SMM, now let's put them into use. The implementation stage—stage 3 of the iterative process—is highlighted in Figure 7.2 and is when you tailor your campaign around how you fit in the market.
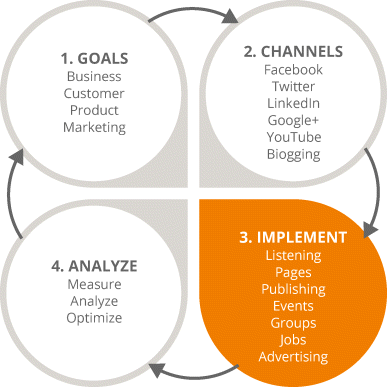
Figure 7.2 Focus on the Third Stage in the SMM Process
In this section you will learn:
· How to understand where your position is in the market.
· The different ways to listen to your audience.
· That careful consideration must be given to your campaign.
Soccer is the number-one sport in the world because of one thing: goals. Once a world-class striker shoots that ball to the back of the net, it's a victory. A soccer game without any goals is a game not worth watching; likewise, in the sport of digital marketing, the more goals the better.
We identified business and marketing goals for social media in the previous chapter, and we looked at the social media channels that most businesses use. So now it's time to channel your inner digital marketing striker: Use social media platforms to your advantage, listen to your audience, and score some phenomenal campaign goals!
Understanding Your Fit
A soccer player does not play a game wearing a kit that is two sizes too small. When preparing an SMM plan, you need to take some time to consider where you fit in the market.
· Where does your audience hang out? Knowing what social media channels are consistent with your audience is very important. Is it one particular channel, such as Facebook, or is it a mixture of various platforms?
· What tone and style of conversation should you use? While a light, fun tone would suit a teenage audience, it would not be appropriate for corporate engagement.
· Who will speak on behalf of your organization? Deciding who will take the reins and be the company's mouthpiece is not a decision to be made lightly, as responsibility and accountability for image management will lie with that person.
· What is the key demographic for your product and how can you reach it? All of the W questions have to be asked: Who are the people in it? What do they do? What do they like? What is their age group? Where do they live?
· How will you respond to negative feedback or comments? Social media communication should engage your audience, and while the aim is always to please the customer, from time to time you might get a negative reaction. If this happens, don't get downhearted; negative feedback can be a key learning tool. That said, you will have to deal with it. The most effective solution is to respond publicly and take the conversation offline as quickly as possible to discuss any issues one-to-one with the customer.
Resources
A soccer team is made up of 11 players, but if all of those players are strikers, who will defend the goal? You may have awesome ideas for your social media strategy, but you need to evaluate what resources you have in order to make sure that every aspect of your strategy will be covered.
People and Skills
The people assigned to the SMM strategy need to be made accountable for shaping, developing, and driving the strategy. When initiating your strategy, figure out whether current team members possess the abilities to see your plan through, or whether training, up-skilling, or hiring new staff members is necessary.
In the same way that not all soccer players are strikers, SMM team members play different positions. You will need people who can take on management duties, people who can engage with customers on a one-to-one basis, people to take control of IT, and people to oversee finances.
Budget
An SMM strategy is a cyclical process and budget is certainly something that needs to be reviewed frequently. Checking analytics is essential; if you find that the initial projection for your budget is too high or too low, action will have to be taken.
Listening
Launching your SMM strategy can be nerve-racking. In fact, it's quite like the start of a new relationship. When you initiate your strategy, remember this: Be a good first date.
A good date is one who listens. Listening to your customers is really important, because you can learn so much from them. The factors to be aware of when listening are:
· What channels to use.
· What tone and style to adopt.
· Whether you are getting different kinds of responses from different demographics.
· Who are the influencers of your target audience and can you leverage them?
By listening to your audience, you find out a lot about your competitors too—there is no hiding on social media! Check out how your target audience reacts and engages with your competitors' social media strategies and learn from their successes (and failures).
Influencers
There's a reason why the town mayor holds public forums: A good mayor wants to keep all of his or her townsfolk happy—and wants to stay in power. When you identify key influencers and listen to them, they can help you, and in return you can give them the product they want.
Engage with Happy Customers
Customers who have had a positive experience with your brand already like your brand. When they talk about you positively, look after them. Like what they say, comment on positive feedback, and when possible, reward them.
Engage with Unhappy Customers
While it's easy to just ignore complaints on social media, don't! If you solve an unhappy customer's problem and win his favor, there is great potential for that customer to become a big advocate of your brand.
Find and Engage with New Customers
Identify potential customers who have complained about a competitor or service and approach them with a solution to their issues.
The reason you listen is to find out what exactly the customer wants—then you can figure out exactly what to deliver. There are two main ways of listening: Being reactive or being proactive.
Being Reactive
Twitter user Alexa Burrows sent a seemingly random tweet lamenting the end of her holiday and jokingly asked airline company JetBlue for a welcome home parade. JetBlue's SMM team was listening and had the exceedingly clever idea to arrange a welcome home party. How's that for service? When you reply directly to social media users who tag you in posts, you build audience trust. So by addressing and solving their problems, you open the door to gaining loyal customers.
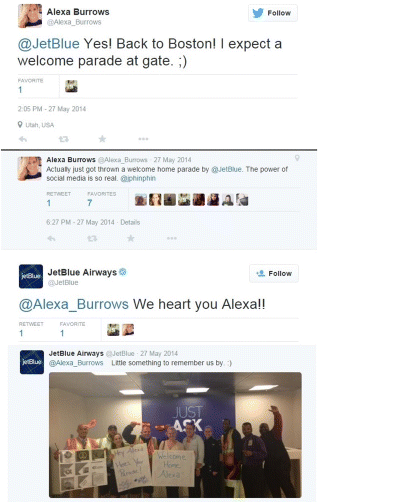
Figure 7.3 An Example of Reactive Tweeting from JetBlue
Source: Twitter.
Being Proactive
Being proactive means working with foresight. During your search for new customers, look for ways to convince them that you have the best service. WestJet, another airline, started an incredible campaign offline. They set up a stall at a boarding gate and asked passengers waiting for their flight what they would like for Christmas. When they landed, wrapped gifts appeared on the luggage carousel—all of the presents that the passengers had wished for. To see the campaign for yourself, type WestJet Christmas Miracle into YouTube (don't forget your hankie!).
Luckily for WestJet, they have the resources (not to mention the finances) to arrange such an effective proactive listening ploy, but even if your budget does not stretch to campaigns like this, you can certainly take inspiration from it.
Tools
In the same way that you can Google any question and find the answer in a matter of milliseconds, one of the great beauties of the digital world is that there are a number of tools you can employ to help you listen to your audience and find out what they are saying about you. Topsy, Klout, Mention, and Google Alerts are some of the best listening tools on the market.
Content Planning
You should let your date do the talking over that first cup of coffee. By listening to their likes and dislikes, you'll have all the information needed to really woo them the next time you meet! The same goes for paying attention to people in your audience: By really listening to them you can gain a lot of important insights, such as what they think of your product and what needs improvement. This, in turn, will help you figure out what type of content to post on your social media platforms. And once you have that figured out, you can begin to formulate your content plan following each of these four stages:
1. Plan it out. As you learned in SMM part 1, scheduling is very important. Create a formal schedule and stick to it as closely as you can. Carefully consider how often you can post on each social media platform and always track each post.
2. Integrate. Your social media plan does not stand apart from your overall marketing campaign—it has to be linked to every other aspect of the campaign.
3. Manage. Use tools, such as Hootsuite, SocialOomph, and Sendible, to schedule social media posts and updates. Using tools like these will also allow you to monitor the level of engagement each post attracts and how many posts is enough (or too much).
4. Adapt. Sometimes you spill red wine all over your mother-in-law's white dress and sometimes you forget to schedule a tweet—but hey, these things happen. In unforeseen circumstances, you need to be prepared to take ownership of the problem, assess your situation, and come up with a way to rectify the missed opportunity.
When creating your content plan, keep these questions in mind:
· What is the purpose of my social media activity?
· Who exactly do I want to “like” my page?
· What content will my audience find valuable?
· Should I create a content calendar?
· How often should I post?
And most importantly:
· What content will my audience engage with?
B2B versus B2C Content
In the context of social media content, think people-to-people rather than business-to-business. Don't aim your content at a faceless company, when in reality you are dealing directly with a person.
In the same vein, think of the market as a community and deliver content that will interest and engage its members. Short and snappy video testimonials are fantastic forms of content. Nontypical success stories work really well for this type of application. For example, instead of posting a video based on a young, privileged Harvard grad making millions of dollars, use an 80-year-old grandmother instead!
Infographics are also a powerful method of compressing a lot of information into one post—information that you know will both interest the people in your audience and (hopefully) encourage them to share. Take note of the following factors when planning your content for each business approach:
|
B2B |
B2C |
|
B2B? Think P2P |
Product or service updates |
|
Community |
Community |
|
Education |
Photos |
|
Industry updates |
Entertainment |
|
Testimonials |
Customer stories |
|
Short videos |
Events |
|
Infographics |
Offers or deals |
|
Customer POV |
Short videos |
|
Infographics |
|
|
Customer POV |
Content Scheduling
The best way to prepare your content is to break it down into a schedule. Take the chart in Figure 7.4 as an example.
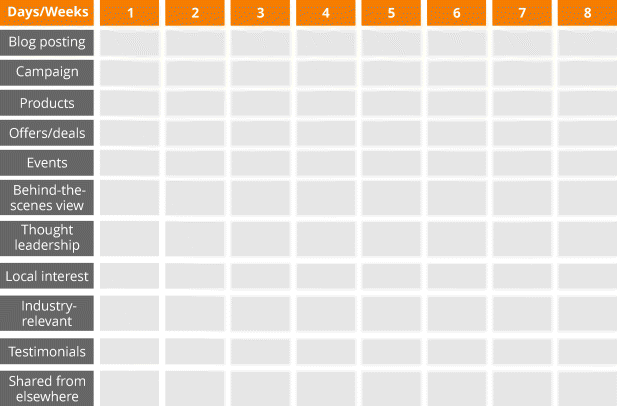
Figure 7.4 Facebook and Twitter Post Scheduling Chart
There are a number of considerations for scheduling content. Think about which network(s) to post to, what tone of voice works best for each, and what time of day is best to reach your target audience. Don't ‘content burst’—it is better practice to stagger your updates so as not to overwhelm your customers with a flurry of posts.
Platform Specificity
There is no monogamy in SMM! You have got to know and love each platform—and then each of them will love you back. Different platforms have different needs and restrictions. Twitter posts have a limit of 140 characters, Instagram is most effective when using multiple hashtags, and certain times of the day are better for posting certain types of content. Take a quick look at Figure 7.5, which shows a post map for Facebook and Twitter and lays out the best times to publish certain types of content.
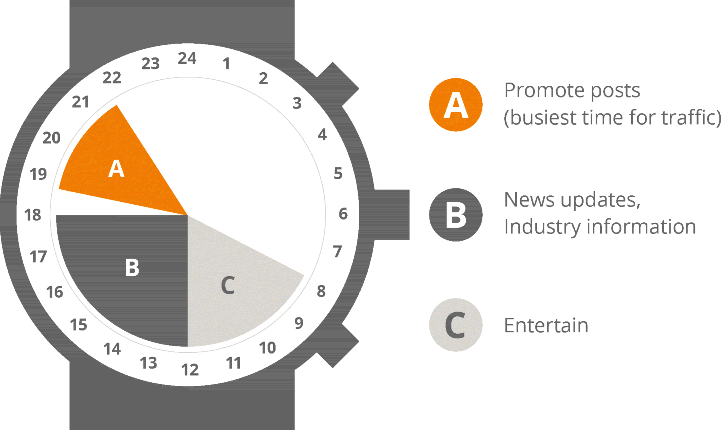
Figure 7.5 Best Times to Publish by Content
Post scheduling of course, is not a cut-and-dry process, so it's always a good idea to use your scheduling tool to review what times and types of posts work best for your audience on each network.
Action Plan
In order for any SMM campaign to be successful, you must acknowledge the constraints that your business has in relation to the time frame available: Don't set a deadline unless you know you can deliver. Examine the resources you have at your disposal—for example, certain parts of the plan may require particular skill sets; do you have a staff member who can perform those tasks? You can think about the actions required to implement the plan once you have considered the other criteria in Figure 7.6.
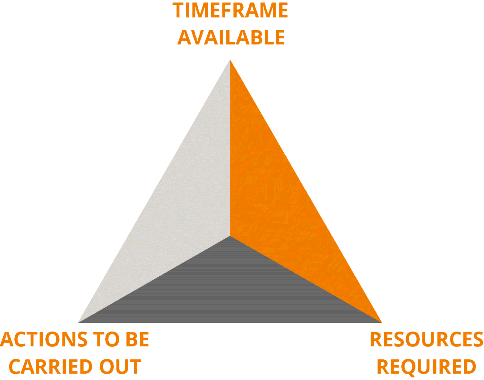
Figure 7.6 Factors Affecting an SMM Action Plan
Marketing Goals
Your goals will differ according to which marketing route you take. Business goals should be set for lead generation, sales, or cost reduction. For customer service, your goals may be about satisfaction ratings, referrals, or repeat business. If you are thinking in terms of your product, perhaps your goals will relate to product research, design, or enhancement. When you think about communication, think about brand personality and reputation management. No matter what marketing road you decide to go down, always keep branding, awareness, engagement, response rate, lead generation, and conversion in the forefront of your mind.
Once you set your marketing goals, the next step is to choose the specific KPIs for each goal. With respect to Facebook, for example, decide what your KPIs are for lead generation—and do the same for Twitter, LinkedIn, and the like.
Social KPIs will be determined by engagement and advertising. For example, with respect to engagement indicators you may look at elements such as reach and follows; for advertising indicators, impressions and clicks may prove the most important. Take a look at the comprehensive list of engagement and advertising KPIs below.
|
Engagement indicators |
Advertising indicators |
|
Reach |
Impressions |
|
Follows |
Clicks |
|
Trending |
CPC |
|
Likes, shares, comments |
Conversions |
|
RT (retweet), favorites, replies |
Conversions |
|
Direct messages |
Registrations |
|
Click-through on posts |
RSVPs |
|
Competition entries |
App installs |
|
Offer redemptions |
Conversions |
Quality Scale of Interaction
Just as a date laughing at your jokes doesn't guarantee a goodbye kiss, for social media, there's a big difference between somebody liking a Facebook post and getting her involved in the conversation. As shown in Figure 7.7, the Like feature on Facebook is the lowest level of interaction after actually viewing the post, and even though the feature is not on all social media platforms, it's still a good way to gauge the quality scale of interaction.
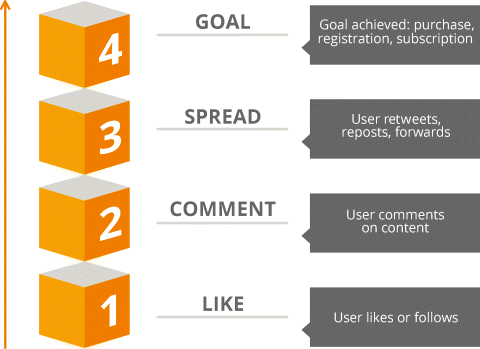
Figure 7.7 Quality Scale of Social Media Interaction
The ultimate goal of posting something on social media is that your audience will see it, engage with it, and spread the word. Each channel is unique and each has different qualities that you need to understand. As we continue through the chapter, let's examine each one in more detail.
Facebook Strategy and Advertising
If social media platforms were high school stereotypes, Facebook would be the homecoming queen.
With over 1 billion users, Facebook rules the social media roost. But Facebook is more than just a pretty face; it is an extremely effective advertising tool and one of the channels used for stage 3 of our process, highlighted in Figure 7.8. This section will burrow deep down to the core of Facebook advertising and at the conclusion you will:
· Be familiar with all of the different types of ads you can run from Facebook.
· Learn the skills required to segment and target different audiences.
· Understand the mechanics of creating a successful Facebook ad.

Figure 7.8 Focus on the Third Stage in the SMM Process
Even if you would prefer to hang out under the bleachers, when you are in business you have to be in with the in-crowd—otherwise, you simply fall behind. Facebook is an incredible tool for delivering messages to your audience: You are not restricted in character count, unlike on Twitter, so you can post a lot of information in one go.
Facebook Page Strategy
The goal of having a Facebook page is to increase interactions. Why? Because the more interactions your Facebook page has, the cheaper your ads will be. When Facebook can actually see the type of people that are interacting and engaging with your posts, they don't have to target the right kind of people on your behalf.
Increasing Your Engagement Level
So how can you grow your Facebook profile to attract more customers?
1. Post consistently and regularly. Schedule your posts for when the majority of your audience is online.
2. Use a calendar to plan ahead. Planning your posts ensures they're in line with your marketing communication goals.
3. Target your posts. Segment your audience into demographic groups and adjust your messaging according. Your posts will only be shown to those fans who match a specific targeting criteria.
4. Use imagery and videos. Facebook audiences love images, and with the autoplay feature, more videos are now being consumed on Facebook than YouTube.
How to Post Consistently and Regularly
Take a look at Figure 7.9. There is so much that you can do with one small text box—add images, show a video, create an offer, and even show emotion.
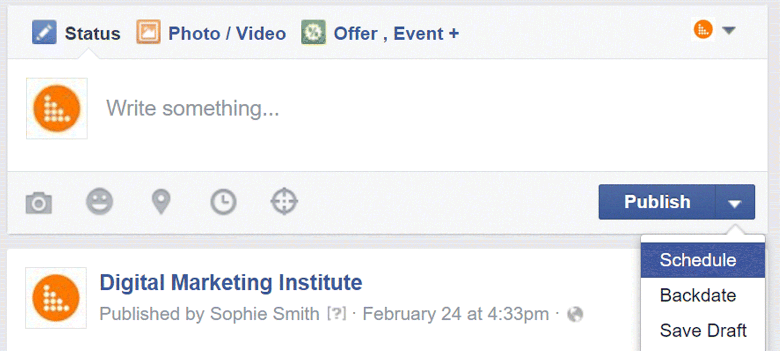
Figure 7.9 Facebook Posting Facility
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
By clicking the little arrow beside the blue post button, you can schedule posts to guarantee that a steady stream of content is being published. Be sure to dedicate some time to organize scheduling, and return at another time to respond to any interactions.
Select Your Audience Carefully
The really cool thing about Facebook is being able to direct your posts to a very specific demographic. If you wanted to let the cheerleaders know there was a big game coming up, you would not announce it to the entire school! The same goes for selecting an audience on Facebook. If you are promoting a product geared towards women in their 30s, you can select that demographic specifically.
You can be very precise about whom you choose to view a particular post. You can narrow it right down to:
· Gender
· Relationship status
· Educational status
· Age
· Location
· Language
· Interests
Say, for example, your business is related to wellness and you are releasing a product related to men's health. By specifically aiming the post advertising the product to your male customers, you go straight to the target audience.
Have a Heart!
When posting, use the features that allow you to add emotions and verbs to describe how you are feeling. Facebook has added this option for a reason: People respond to emotion and they appreciate a personal touch. Staying with the personal theme, it is a good idea to publish behind-the-scenes photographs of your company. It helps customers relate to the company on a deeper level.
This option shows just how incredible Facebook is as a digital marketing tool. Companies do not have to be faceless institutions anymore: Letting customers in on the people behind the company brings them closer to the brand.
When the Price Is Right
While it's true that Facebook is a fantastic tool for businesses to get new clients and generate revenue, it is getting harder to reach your audience for a number of reasons.
· Users began to complain that their News Feeds were becoming clogged up with promotional content and Facebook listened. Over the past few years Facebook has reduced the number of people who actually see a post, even if they are fans of your page.
· Facebook did not just change its algorithm for the good of its users—it saw a financial benefit for itself.
Right now, because of updates to Facebook's EdgeRank algorithm, ordinary users will see less promotional content on their news feeds. In fact, only 8 percent of people who “like” your page will see a post. That is an extremely low percentage, but there is a solution—adapt and pay. To get any significant impact out of Facebook, you need to spend money with Facebook.
Boosting Your Post
There are many different ways to advertise on Facebook, but let's start with boosting—the mechanism that allows you to sell without selling.
Boosting a post is the easiest form of Facebook advertising and it's an extremely useful one to use during an important promotion. It is a good way to introduce yourself to Facebook Ads and to learn how it works.
The process is simple; follow these three steps:
1. Click the Boost Post button under the text box.
2. Choose which audience you want to target.
3. Choose how much you want to spend and how many days you want to boost the post for.
It's worth being strategic about which posts you boost. View your post history to see the types of posts people interact with, how many people view video posts, and which type of posts get the most shares. Popular posts that haven't been boosted give a good indication of how well that type of post would do if it were to be boosted. When you are starting out and familiarizing yourself with Facebook advertising, boost at least once a week. This will let Facebook know that you are a spender rather than someone who uses the platform for free.
Facebook Ads
Boosting may be the easiest way to bring attention to your Facebook page, but there are multiple other advertising routes to take and all of them serve a specific purpose. The ad in Figure 7.10 is designed to encourage people to click through to the website. Pay attention to the word Sponsored in the top left-hand corner. This word appears on every Facebook ad so that people will know that the post has been paid for. The ad in Figure 7.11 is a video ad—see that little play button on the image? This is a good way to provide your target audience with educational content—ideas that they can share.
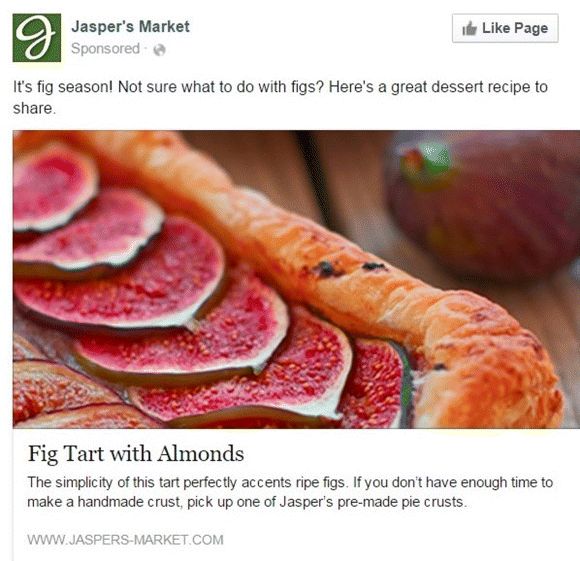
Figure 7.10 Clicks to Website Facebook Desktop Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
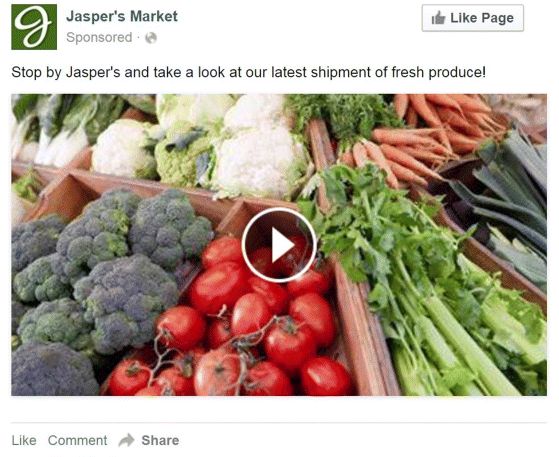
Figure 7.11 Video Views Facebook Desktop Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
The ad in Figure 7.12 is an ad with a Use App button (bottom right) that encourages people to install an app. Figure 7.13 is an example of an event ad—which is an interesting ad type, as it lives online but gives you the chance to meet your customers in person. And finally, Figure 7.14 illustrates another type of ad—the offer. This is a popular type of ad, as it provides something useful to the customer and it enables you to collect useful information, such as email addresses.
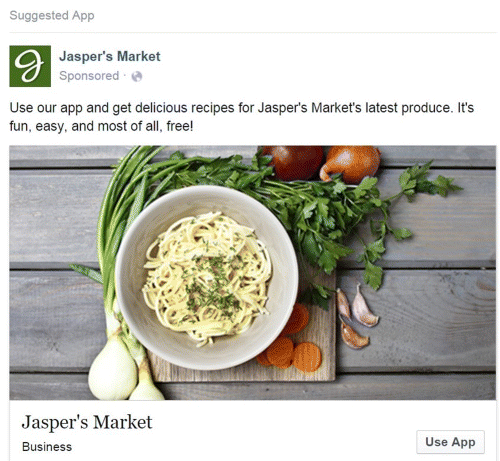
Figure 7.12 App Installs Facebook Desktop Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
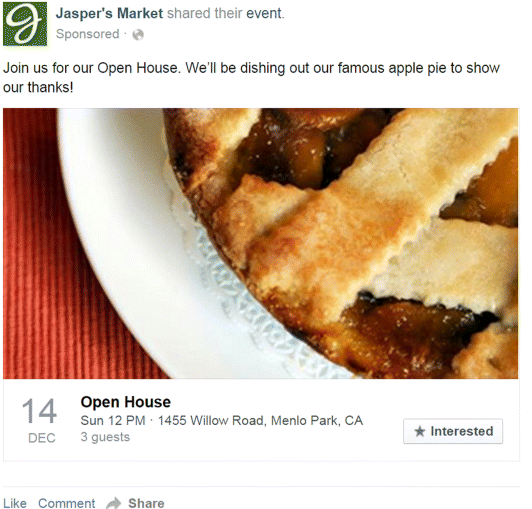
Figure 7.13 Event Response Facebook Desktop Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
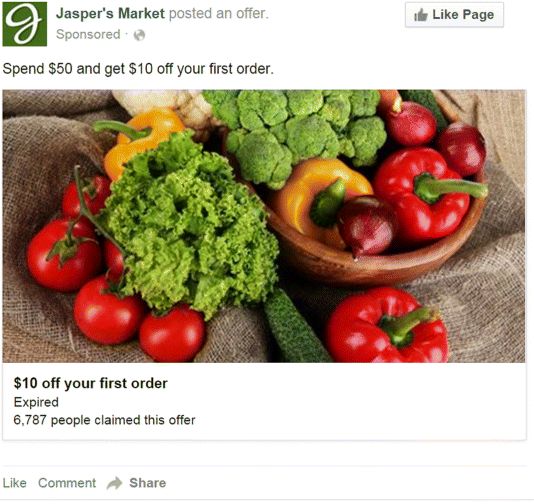
Figure 7.14 Offer Claims Facebook Desktop Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Ads Manager
The Ads Manager function allows you to set up any type of ad you choose. Before you can use it, however, you need to create the ad, so that you can register your credit card details. There will come a stage when you may have multiple ads running at the same time—and here is where Power Editor comes in. Power Editor is the most convenient place for managing your ads, allowing you to manage all ads in one place and to make changes very easily. Be aware, however, that Power Editor can only be used with the Google Chrome browser.
Audience Insights
Audience Insights helps you to define the size of your target market and to target ads more specifically to your audience. Narrow down your audience by choosing from a range of options, including interests and behaviors, age, gender, location, work information, relationship status, and family. Check out the Behaviors feature of Audience Insights, which allows you to specifically choose people who have already spent money on Facebook. It also allows you to segregate higher-than-average spends on Facebook—pretty nifty, right?
The first step is to choose your audience, as shown in Figure 7.15.
Figure 7.15 Choose your Audience for Facebook Insights
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Next, define your audience attributes. You will see from your demographics what kind of people are already on your page. In Figure 7.16 you can see that 49 percent of users are female and that 25 percent of those women are in the 25-to-34 age cohort.
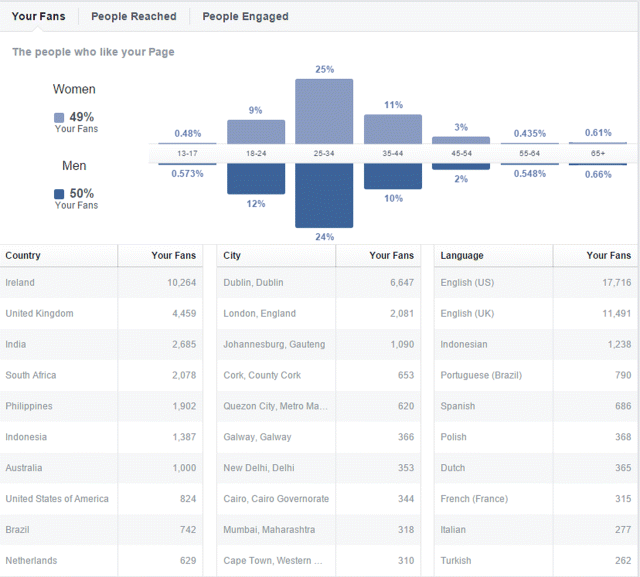
Figure 7.16 Facebook User Demographics
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Then if you want to get really specific, you need to target your audience according to lifestyle. For example, if you are in the business of pensions, you might want to target the Raisin' Grandkids lifestyle group, as seen in Figure 7.17.
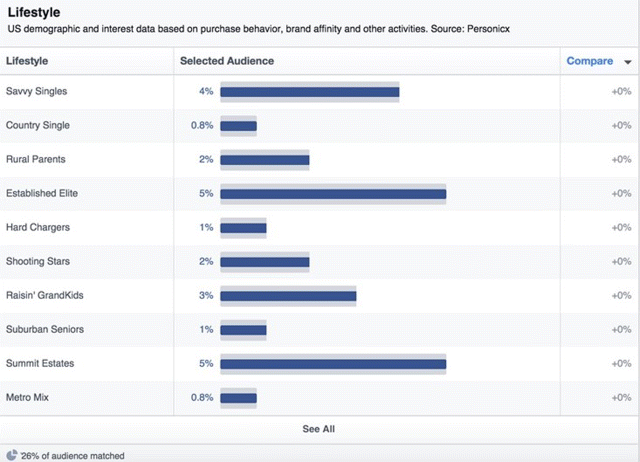
Figure 7.17 Facebook Insights Lifestyle Report
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Objectives
When you first create an ad, Facebook will display a list of objectives for you to choose from, as illustrated in Figure 7.18.
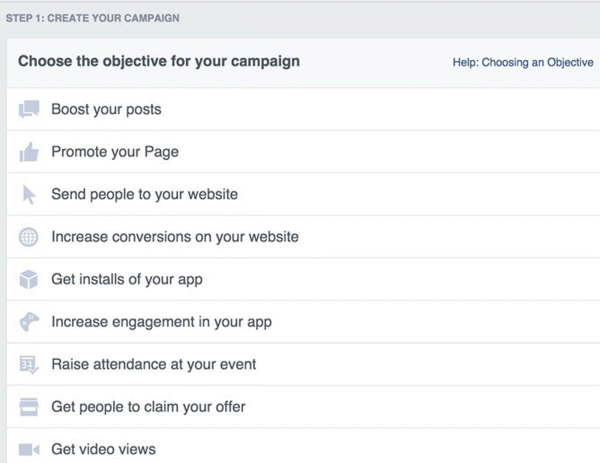
Figure 7.18 Choosing an Objective for a Facebook Ad
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Choosing which objective is best differs from business to business. If your sole objective is to increase the number of clients you have, compare various types of ads to discover which are giving you the maximum ROI. The best way to do that is to use Power Editor, which allows you to monitor multiple types of ads all at once and compare the ROIs of each. When you have discovered the best way to make more than you are spending, you'll know which objective is best for you.
Audience
After you have decided on your objective, the next step is deciding whom to target. Once you choose the specifics—age, location, gender, education level, and interests—take note of the speedometer on the right.
Make sure that the pin is smack bang in the middle of the speedometer, as in Figure 7.19—if it is too far to the right, your reach will be too broad; too far to the left and your reach will be too specific. The aim is to have an evenly defined audience. You will have to test different things to center the pin, such as changing the level of education or adding more interests to make sure that pin is hitting the 12 o'clock mark.
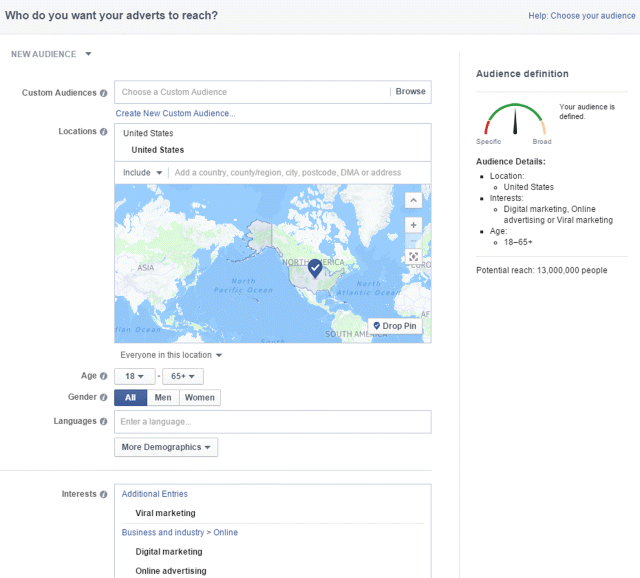
Figure 7.19 Facebook Speedometer Ad Targeting Gauge
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Advanced Training
Facebook's custom targeting function allows you to reach a highly specific audience. The catch is, you must have an email database. By uploading email addresses from your database, Facebook will be able to run an ad campaign that will appear right in front of those people. Not only that, Facebook gives you the option of displaying your ad to those who match the likes and interests of those on your email list, and this can be done whether they “like” your page or not.
Another fantastic feature is the Facebook pixel, which remarkets to people who may have visited your website because of a Facebook ad but who did not fulfill your call to action (CTA). Installing the pixel will assist in bringing visitors back to your website and in finding new customers who fit your target audience specifications. Always perform split testing with your ads to work out which one is getting a better response. Run at least two ads at the same time and use a combination of multiple images and various CTA buttons to do comparisons so you can see what is and is not working.
Writing the Ad
Once you have locked down the type of ad you wish to create and the audience you wish to target, it's time to write your ad. Writing your ad follows the same rules as any type of advertising—an eye-catching headline and compelling text—but there are limits. The headline can be up to 25 characters and the text up to 90 characters. If you are stuck for ideas, “like” the pages of your competitors. By doing so, their ads will appear in your right column and on your cell phone. Pay attention to threads that are being run often because they are most likely to be performing well, meaning the copy is well written and engaging.
Budget Setting
To define your ad, decide on the daily budget and the maximum budget per interaction, page “like,” and link click. From this, set a schedule to determine how long the campaign is going to last. Before running a campaign over a long period of time, test it by running it for a week to see what works. Edit, modify, and improve it until you are sure it is primed and ready to go.
Reports and Insights
The Reports and Insights function not only details your results, but also tracks how well your ad performed. You can set a schedule in Facebook to receive reports with your ad results via email at a specific time so that you never forget to monitor ad performance.
Places
If your business is a physical location, register it on Facebook Places so that your customers can check in. Each check-in is marked as a visit on your Facebook page, and users can tag photos, status updates, videos, and so on from your location.
Facebook Groups
Aside from advertising, Facebook Groups is the only other element of Facebook where you can generate an income from your client base, as ads are not yet limited. Better still, it's free!
Groups can be closed (users must submit a request to join), secret (users can only be invited to join), or public (open to everyone who wishes to join). Facebook groups are useful for a number of reasons: You can develop a network of like-minded users, collaborate with industry peers, or just be part of a community that is linked to your business and listen to what is going on. Try joining a number of groups to figure out what is driving discussion and then create your own based on your findings.
Apps
The benefit of adding apps to your Facebook page is essentially to make it a mirror for your website. An example of a useful app is an HTML tab. This can be used for a menu if you run a restaurant or a price list for a service such as a hair salon. It is also possible to set tabs for webinars, for selling products, for an opt-in page (where people can sign up for free gifts), or a Contact Us form.
In general, you can do anything that you can do on your webpage on your Facebook page by using third-party apps. To name three examples, you can host a YouTube channel using Probist or Cueler, run contests using Woobox, or host a webpage within your page using Thunderpenny.
A business that does not possess a Facebook page is at a huge disadvantage. A business that does not use the advertising mechanics of its Facebook page should not be in business! Social media advertising may be a relatively new format, but it is extremely important. Facebook is the top dog at the moment, but that does not mean that it should be the only one. As long as there are social media platforms, there are opportunities to promote your business. Let's move on to the next section and see what LinkedIn can do for you.
LinkedIn Advertising
If Facebook is Social Media High School's queen bee, LinkedIn is that whiz kid who made a million dollars before she even graduated.
LinkedIn is different from other social media platforms because the audience it attracts is already a specific target: the workforce.
The average user on LinkedIn earns over $100,000, making it the most important social media platform for the corporate world. Why wouldn't you advertise on this platform?
In this section we will navigate through the ways you can use LinkedIn to promote your business, and by the end of it you will:
· Be adept at joining and creating groups.
· Know the best practices to ensure strong engagement within groups.
· Understand the best ways to search for a job on LinkedIn and to find your next hire.
· Master the mechanics of creating the various types of advertisements on LinkedIn.
If you have a business that thrives on industry discussion, you cannot neglect LinkedIn. While it may not be as fun as Facebook or Twitter, it is extremely useful for making vital connections with other leaders in your industry. Having a presence on LinkedIn not only proves you are serious in and about your industry, but also could attract the next bright spark to join your team.
LinkedIn Groups
LinkedIn groups are very similar to Facebook groups: You can join those that already exist or you can create your own. There are two types of LinkedIn groups: private (you submit a request to join or are invited to join) and public (anyone can join). The discussions that take place in LinkedIn groups are led by those in the industry, and the best discussions are those that really engage the group. Some groups allow you to post promotions or to run advertisements for jobs when you are hiring. And when you master the art of engaging discussion, you can post these promotions seamlessly in your group.
Leader of the Pack
By participating in group discussions regularly and delivering quality input, you grow your position as a top contributor. This high level of engagement in discussions is the best—and fastest—way to grow your number of connections on LinkedIn.
So how can you connect with group colleagues who have similar interests? LinkedIn Connect. To connect with like-minded LinkedIn users, simply type in the keywords for the type of group you are interested in, and when the list appears it will show which groups you belong to and which of your contacts also belong. Then just join a discussion, become known in the group, and work your digital marketing magic.
Creating a group is also simple. Just navigate to the Create a Group button, as shown at the bottom of Figure 7.20. When you click on it, name the group, decide on the group type (public or private), give a summary of what the group is about, and insert a link to your website.

Figure 7.20 How to Create a LinkedIn Group
Source: LinkedIn.
Group Access
Depending on whether you want an exclusive, invitation-only group or one that will accept anyone who is interested, set the group to either public or private. You can also set membership policies and you can preapprove members by email address or email domain.
Promote
When you are starting out in a LinkedIn group, get involved, learn the ins and outs, and get the general discussion going. Only when you have got into the discussion flow should you promote your post. Again, it's very easy to do. At the bottom of the Start a Discussion box shown in Figure 7.21, you can choose the type of discussion (general, job, or promotion)—just select the Promotion button when you wish to promote! Create the title and details around that.
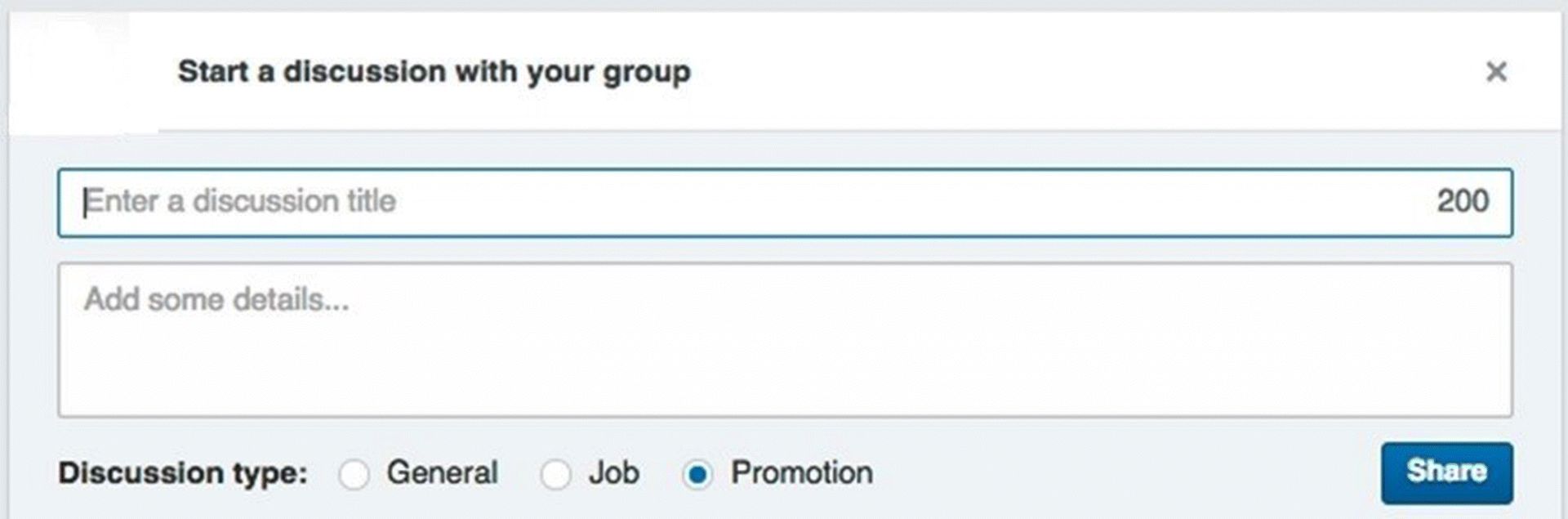
Figure 7.21 Start a LinkedIn Discussion and Choose Discussion Type
Source: LinkedIn.
Searching
To search for companies, jobs, or groups, use the large search field on the very top of a LinkedIn page, illustrated in Figure 7.22. To look specifically for people, use the advanced search function, which is to the right of the magnifying glass icon.
Best-Practice Tips for Searching for People on LinkedIn
The beauty of LinkedIn is that you can really hit the bull's-eye when searching for people. The way to do this is to use quotation marks to get specific results about a specific type of person. For example, if you are looking for a social media manager, search for “social media manager.” Type or between terms if you are looking for multiple synonyms for skills or job titles.
Take a look at Figure 7.23 to see exactly how it works. As you can see in the Title text box, the title social media manager is enclosed in quotation marks with the word OR written after it (after that is something like “community manager” or “digital marketing manager,” also enclosed in quotation marks).
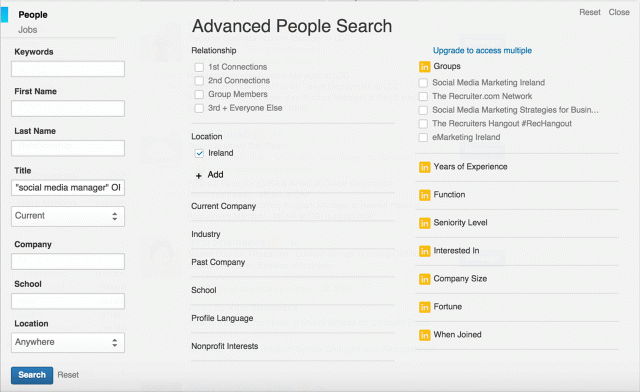
Figure 7.23 Strategies for LinkedIn Advanced Search
Source: LinkedIn.
You can also exclude classes of people from a job search. If you don't want trainees, for example, just type the word “not.” That way you can filter results and come up with only the kind of people that you are looking for.
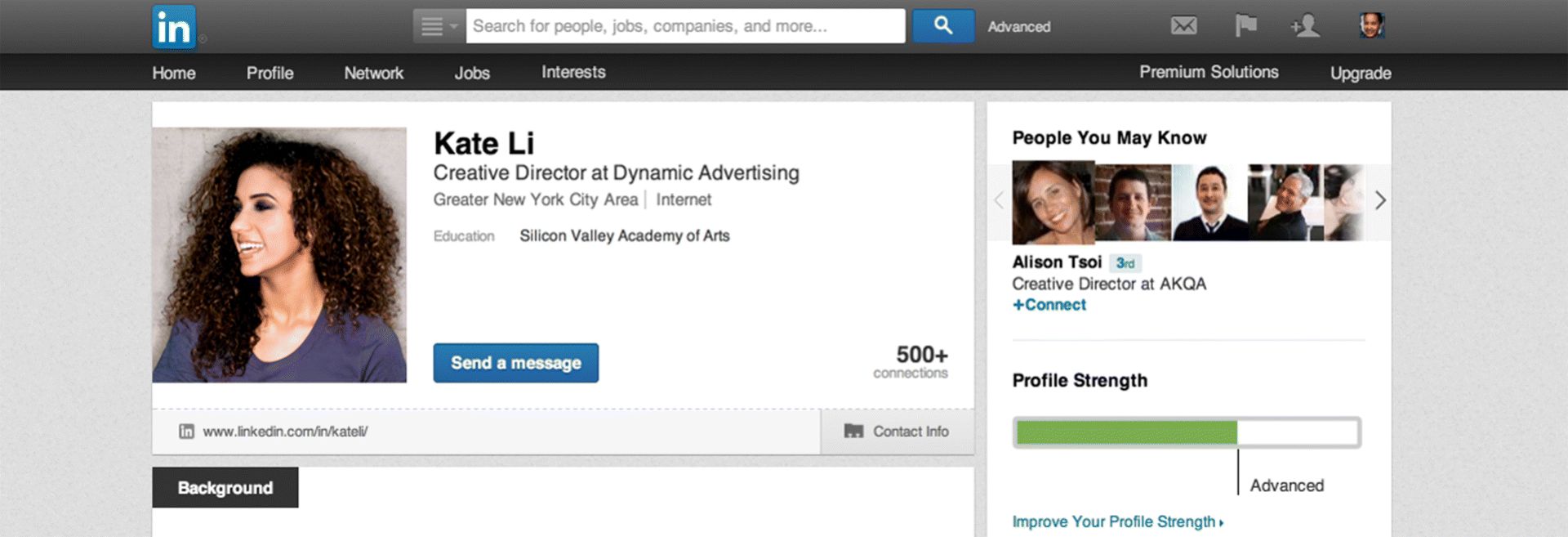
Figure 7.22 LinkedIn Search Field and Advanced Search Function
Source: LinkedIn.
LinkedIn Premium
A LinkedIn premium account has extra features for business professionals. For one, you have access to more profiles when you search (you can only see up to 100 profiles on a free account). In addition, you can see who has viewed your profile insights over the past 90 days, save important profiles, and add notes to profiles using the profile organizer.
There are even higher levels above LinkedIn Premium: With the LinkedIn Recruiter and LinkedIn Sales Navigator options, you can see the full profiles of anybody on the LinkedIn network, regardless of whether they're a connection.
Using LinkedIn to Search for a Job
One of the main purposes of LinkedIn is to search for and apply for jobs. Based on a user's profile, LinkedIn will suggest the most appropriate jobs to each member and will alert members about new, relevant jobs by email. If you have a LinkedIn premium account, your application can be flagged as a featured applicant, so that you will stand out. Premium members can also get insights about job roles before they even submit a job application. Businesses can advertise jobs on LinkedIn and receive applications through both traditional CVs and their LinkedIn profiles.
To look for a job, type the job title by keyword or company name and then fill in the rest of the information, such as the location in which you would like to work and the size of the company and the industry you are interested in. Click Finish and LinkedIn can work from there.
Using LinkedIn to Find Your Next Hire
As seen in Figure 7.24, LinkedIn guarantees at least 10 applicants for every job that you post, and it will manage the job application process and give you a ranking of each application based on the applicant's profile versus the job description. Your job ad will also be promoted on appropriate candidates' news feeds and by email update.
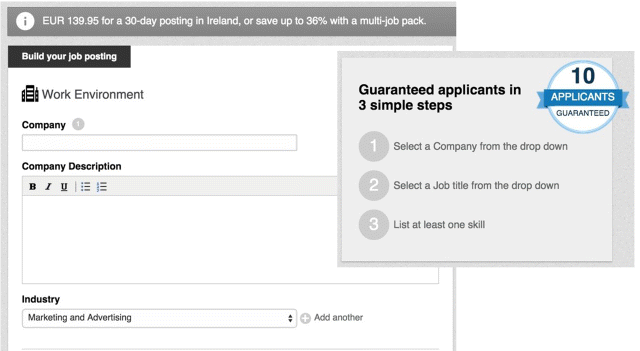
Figure 7.24 Posting a Job on LinkedIn
Source: LinkedIn.
To post a job on LinkedIn, first choose your company by typing it into the text box and selecting it from the list. Next, choose a job title so that LinkedIn can better match your job with potential applicants. Write your job description and details and choose whether you prefer to receive applications directly via email or at your company's career site.
LinkedIn Advertising
LinkedIn ads enable you to target LinkedIn members based on a number of demographic criteria: location, age, gender, company, education, industry, job title, and even a specific job function.
When deciding on the cost of the ad, you are given two options to bid for your ads: cost per click (CPC) or cost per thousand impressions (CPM). Before you gain experience, be careful when choosing which option you want. Many people think that choosing to pay for CPM is the better option because it looks cheaper; however, bear in mind that an impression is defined as every time the ad is shown. So, even if you choose to pay $2 per 1000 impressions, the same person might see the ad multiple times—in which case many of these impressions will not result in any action being taken. Until you get really good at your ads use CPC, because at least then you know that you are getting clicks. CPM becomes much more valuable when you know how to write an ad that gets people to click. When deciding on a suggested bid range, go to the higher end of the scale. Why? Because LinkedIn then knows you are serious. The Suggest Bid Range field helps you to choose a number based on competing bids from other advertisers. By bidding a higher number, not only will you outbid everybody else, you will get preferential treatment from LinkedIn—and you still won't actually pay the highest price.
Sponsored Content
LinkedIn supports multiple advertising formats, including sponsored updates on your company's LinkedIn page, which is similar to Facebook boosted posts, so rather than creating an ad, you may sponsor content instead. Simply choose which piece of content you wish to promote and the audience you would like to target, as shown in Figure 7.25. Decide on how much you would like to pay per campaign, check out, pay up, and your ad is ready to go!
Best Practices for a Strong Ad
Your ad will have a lot of competition—so how do you make it stand out from the crowd? Ensure that your headlines, copy, and images are as clear and attractive as they can be. Look to your main competition for ideas: Draw inspiration from the pictures they use, and the titles and text that they write.
1. Headline. Choose a strong, catchy title.
2. Copy. Split test your ad to target different demographics and determine which ad works best. Always include a CTA and let people know exactly what they need to do. By telling your audience to do something specific, you immediately get a higher turnaround rate of people taking that action.
3. Image. Choose an image that means something to your audience: a person, or an example of your product, for instance. You only have 50 pixels squared, so try to make it stand out.
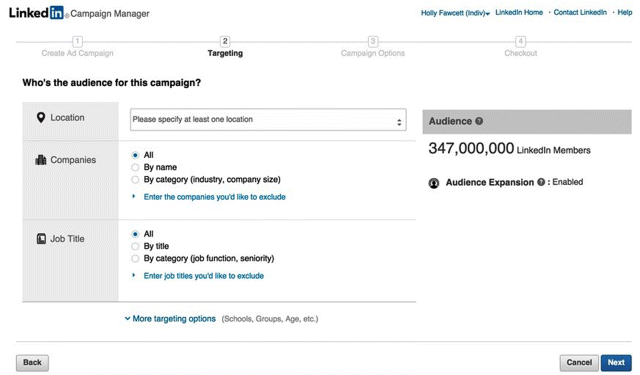
Figure 7.25 Sponsoring Content on LinkedIn
Source: LinkedIn.
Sponsored InMail Campaigns
LinkedIn gives you the opportunity to send direct emails, or InMails, to whomever you want—even if they are not your connections. This can be very powerful, especially if you want to target a particular audience in a localized market. Within the InMail, there will be a clickable icon that gives the email recipient the opportunity to follow through on a CTA, which always improves conversion rates. You should note that sponsored InMail campaigns are not available through the normal self-service advertising platform, to avail yourself of the service you need to contact LinkedIn's marketing solutions area.
LinkedIn KPIs
Choose specific indicators for each of your marketing communication goals: For advertising indicators, use the number of impressions, number of clicks, CPC, click-through rate (CTR), and number of leads or contacts gained. Keep a close eye on your CPM and CPC. Your personal LinkedIn account provides information on profile engagement and connections. Growth of the company page and the number of followers is something you can also monitor, along with the company page engagement with posts.
|
Advertising Indicators |
Account Indicators |
|
Impressions |
Your Personal LinkedIn Account |
|
Clicks |
Company Page Growth in Followers |
|
Cost-Per-Click (CPC) |
Company Page Engagement with Posts |
|
Click-Through-Rate (CTR) |
Leads (contacts) |
While Facebook may be the top dog when it comes to SMM, LinkedIn is the smart dog. There are no disadvantages to advertising on this platform; when done right it can make your business stand out amongst your peers and potential hires, which can only be a good thing.
If Twitter were in high school it would not be part of any clique. With its strict character limitations, Twitter is the smart wisecracker who can deliver a witty one-liner. It is not as popular as Facebook, but still, almost everyone wants to hang out with it. Just because businesses aren't riding on its coattails as with LinkedIn, Twitter is definitely something that is worth your while to spend time, resources, and money on.
This section will tunnel through how advertising on Twitter is of benefit to your business, and when we reach the light at the end, you will:
· Be an expert at creating all three different types of Twitter ads.
· Know how to analyze the activity dashboard and measure what works best for you.
· Be able to choose the best type of tweet to promote.
Twitter Advertising
There are three main promotions you can do on Twitter: Promote a trend relating to your business or event, promote your account to get more followers, and promote a tweet to get engagements or a specific CTA.
Take a look at Figure 7.26: It shows a promoted trend with the hashtag #ILoveCoffee. It is obvious that it is promoted due to the yellow arrow icon. Figure 7.27 suggests a certain Twitter account to follow. Figure 7.28 is an example of a promoted tweet, which advertises a language school. It is quite easy to promote a trend or account, but promoted tweets and Twitter cards take a little more effort. So let's take a closer look.
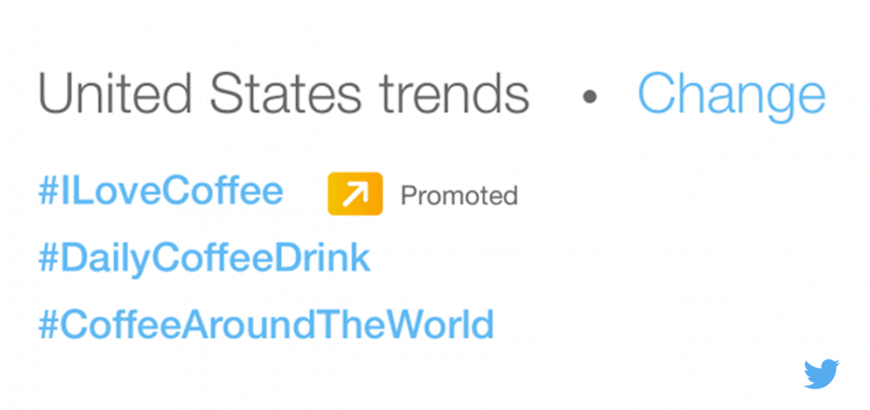
Figure 7.26 LinkedIn Promoted Trend
Source: Twitter.
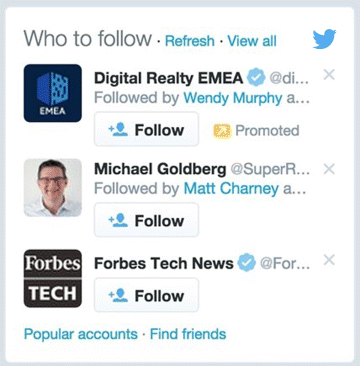
Figure 7.27 Users Twitter Recommends that You Follow
Source: Twitter.
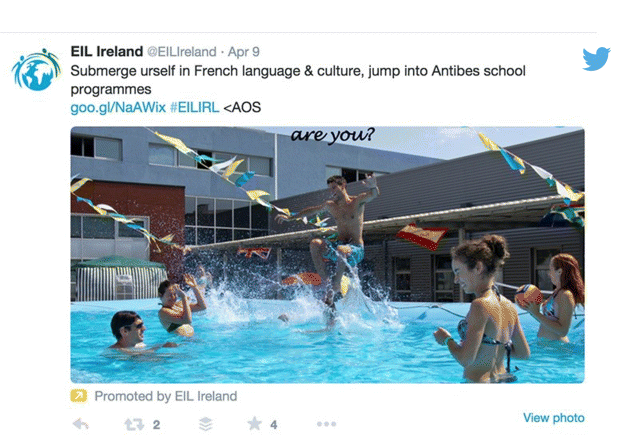
Figure 7.28 Promoted Tweet for a Language School
Source: Twitter.
The promoted tweet in Figure 7.28 has a large image and a clearly defined link to the website, but no CTA; the tweet itself would have appeared on the tweet stream of members of the target audience. For this type of Twitter ad, the advertiser is charged by Twitter on a cost-per-engagement basis, so if Twitter users interact with this sponsored tweet—by favoriting, replying, or retweeting, the promoter pays.
Creating the Ad
The first thing you are asked to do when creating an ad is to decide on a name for your campaign. Next, choose to either compose a tweet, as shown in Figure 7.29, or select a tweet that you have already written (usually one that has received the most organic engagements).
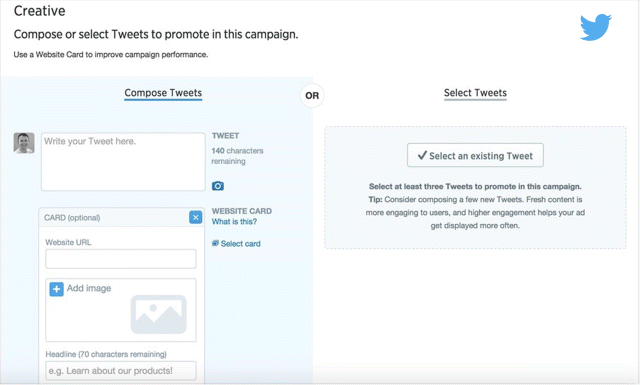
Figure 7.29 Creating a Twitter Ad
Source: Twitter.
Next, select the location and after that select additional targeting criteria: keywords, followers, interests, tailored audiences, and TV targeting. Given the in-the-moment nature of Twitter, TV targeting is very interesting. It allows you to specifically target a TV program on a particular night, on a particular channel, and to run your ad only during that time. Anybody who is discussing or engaging with that TV program will therefore see that tweet in their streams.
Creating a Twitter Card
The most popular form of promoted tweet is the Twitter card, which features a CTA to encourage app installs, websites visits, lead generation, and so forth. This is the best way to collect email addresses, grow followers, or increase engagement with a particular tweet.
Creating a Twitter card is a really straightforward process, as illustrated by Figure 7.30. Insert your website URL, add an image (800 × 320 pixels), type in your headline, and choose from the variety of CTAs, such as read more, shop now, view now, visit now, book now, learn more, play now, bet now, donate, apply, quote, or book.
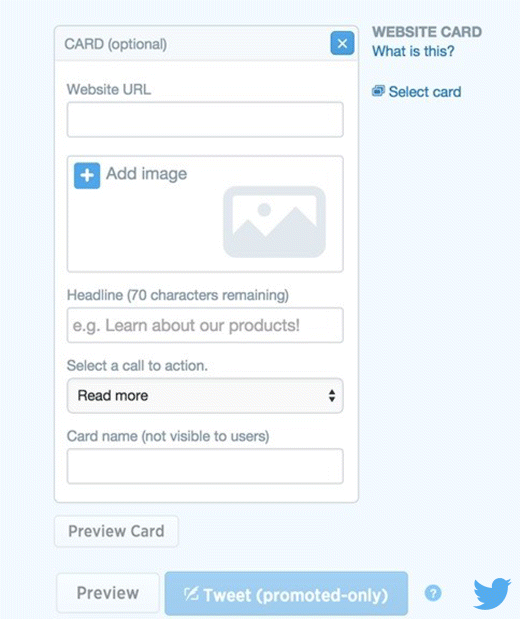
Figure 7.30 Creating a Twitter Ad
Source: Twitter.
Get ideas for how to do Twitter cards well by observing Twitter cards that appear in your own stream. They are such a snappy way of getting attention, and as they are not yet being overused, they are seriously effective ways to advertise your brand.
Tweet Activity Dashboard
As mentioned earlier in the section, you can choose a previously published tweet to use as your promotion. Choose which tweet is worth promoting by looking at the Twitter Activity Dashboard, which gives you a lot of useful information, such as how many profile visits your page had, how many new followers you gained, and how many tweets linked back to you. The graphs in Figure 7.31 measure and clearly lay out engagement rate, retweets, replies, link clicks, and favorites, so that you can analyze exactly what information that you need.
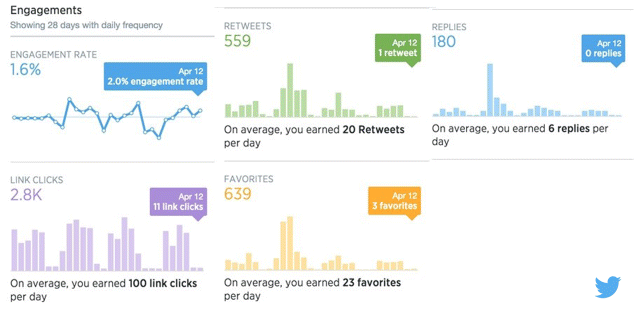
Figure 7.31 Twitter Activity Dashboard
Source: Twitter.
Twitter KPIs
If you are looking at advertising indicators, the KPIs you should monitor are impressions, clicks, CPC, cost per engagement, and conversions. In terms of your account KPIs, observe things such as how many replies you got, how many mentions, and how many follows or unfollows. Check out these lists of the most important KPIs for advertising and for accounts:
|
Advertising KPIs |
Account KPIs |
|
Impressions |
Replies |
|
Clicks |
Mentions |
|
CPC |
Follows/unfollows |
|
Cost per engagement |
Tweets |
|
Conversions |
Retweets |
|
Clicks on a Tweet |
|
|
Direct message |
|
|
Favorites |
|
|
Trending |
Twitter is the epitome of society today. It is fast paced, it has its finger on the pulse, and it bores easily. When you learn the knack of producing snappy Twitter ads that your audience will be happy to click or engage with, you are on to a winning strategy. We have looked at Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter in some depth now, and while it may seem like keeping up with the Kardashians is more manageable than keeping up with these platforms, don't flake out on us just yet! There are even more social media platforms with advertising abilities that could be of major advantage to you. Let's carry on to the next section and check them out.
Additional Platforms
At this stage we know that social media is a veritable Breakfast Club. Facebook is the most popular, LinkedIn is the smart one, and Twitter is the class clown. It doesn't stop there, however; there are many more platforms out there, all with distinct identities that you may use to your digital marketing advantage. Let's wander down the path of social media discovery and at the end of it, you will:
· Be familiar with the advertising mechanisms offered by YouTube, Instagram, Pinterest, and Snapchat.
· Understand which platforms best suit your industry and audience.
YouTube
YouTube needs no introduction—along with Facebook it is one Internet success story that everyone has heard of. If Facebook is the homecoming queen, YouTube is its date at the prom! As the way we consume information evolves, people are becoming accustomed to using video rather than text—so if you are not already on the video bandwagon, you should be. YouTube is owned by Google and it uses the Google AdWords platform, so in order to use it successfully, you will need to be registered with Google and comfortable with Google AdWords.
There are three main types of ads available: those that appear in search results, those that appear before videos, and those that appear alongside videos. Take a look at these images to get an idea of where the ads would be placed.
Option 1: In Search Results
Note the highlighted videos in Figure 7.32. These are ads that appear first because an advertiser has paid for them to appear before organic search results.
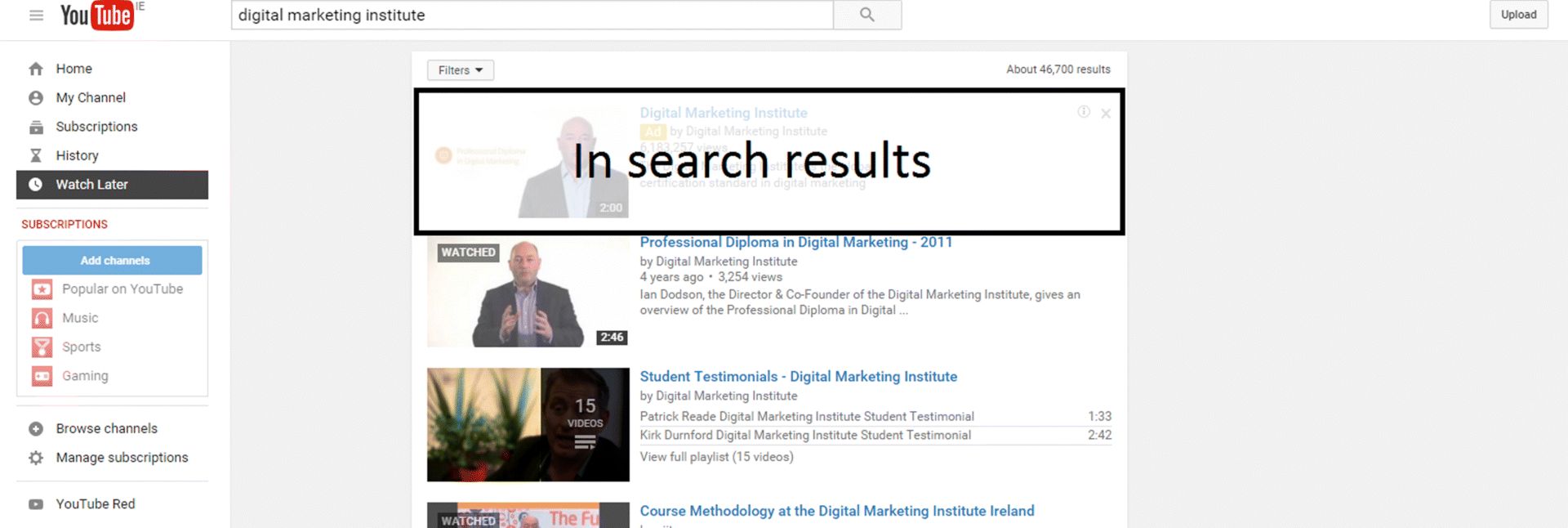
Figure 7.32 In Search YouTube Ad
Source: YouTube.
Option 2: Before Videos (Rolling Ad)
This type of ad is shown in Figure 7.33 and plays before a chosen video, particularly if that video has a high number of views. There will normally be a countdown of five seconds before the viewer can stop the rolling ad.
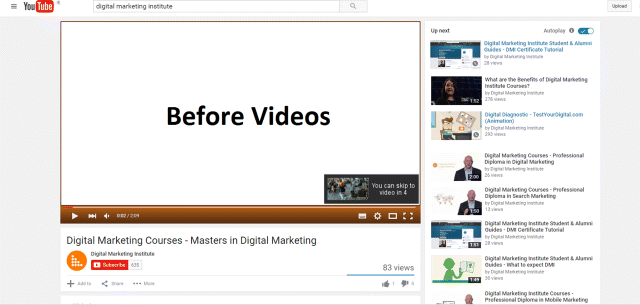
Figure 7.33 Before Video YouTube Ad
Source: YouTube.
Option 3: Beside Videos
As shown in Figure 7.34, rather than having your ad play before a video, you can place it on the right-hand side of the video.
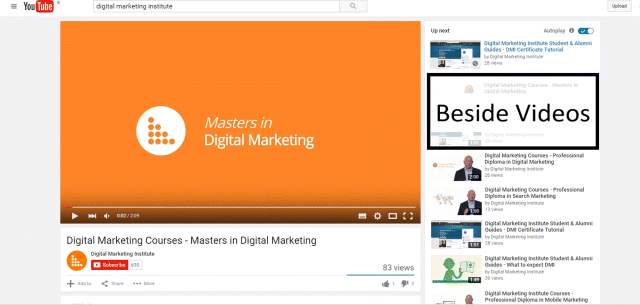
Figure 7.34 Beside Video YouTube Ad
Source: YouTube.
Each ad has its own benefits but the only way to figure out which method works best for you and what will bring the best ROI is to test and test again!
Pinterest is an image-driven social networking site with over 72 million active users—and growing. In fact, it is the fastest-growing social network platform. It has a female-dominated user base, so although the male user base is growing, it is definitely worth considering if your audience is primarily female. Interestingly, 80 percent of Pinterest usage takes place via cell phone. It is also a popular platform amongst people in their 40s and over, because unlike Facebook it is more about sharing ideas than revealing personal information. In this way it is very good for driving targeted traffic. If that isn't enough, this reason might convince you to adopt Pinterest into your social media campaign—out of all the other social media sites that are being used, Pinterest has the highest ratio of buyers.
Let's think of Pinterest as the homecoming queen's best friend—the nice, organized one who decorated the gym for the prom. Pinterest is a hobby and ideas platform, which can certainly be used to business advantage. In fact, there is a conversion function on Pinterest to turn a regular Pinterest account into a business account. (If you don't already have an account, you can go straight to setting up a business account.)
Pinterest Analytics
A Pinterest business account's analytics page displays the average daily impressions, average viewers, and average monthly views. It also gives a breakdown of each pin you put up: How many impressions it got, the number of re-pins, the number of people who clicked, and how many people liked it.
Signing Up for a Pinterest Business Account
This process, which is shown in Figure 7.35, starts on the left-hand side of the page, in the Help People Discover box, with the Install Pin It button (when an image has a Pin It option, anyone can pin that image to a board on their Pinterest accounts). Next, it asks you to Spread the Word by installing the Follow Me button. Then you need to verify your website to Track What Works so you can start to track how many clicks you are getting directly from Pinterest users. To do this, you will receive a piece of code to insert into your website.
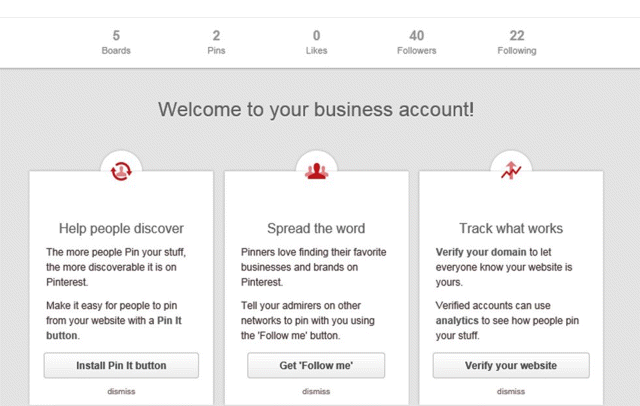
Figure 7.35 Pinterest Business Account Set-Up
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Pinterest.
So you have got the pins but where to pin them? On a board of course! One of the nice things about Pinterest is that it harks back to the good old days of pinning a postcard or shopping list to a corkboard in your kitchen. With Pinterest, however, you don't have to place your bathroom conversion ideas with your inspirations for wedding dresses —you can create a variety of different boards based around different topics. As far as your business account in concerned, keep it simple to begin with—but set up at least three boards, one about your business, one about humor, one about your niche in general and what's going on in your business. Keep in mind that the highest number of posts that are shared relate to cats, followed by posts about dogs. So if you can relate your business to cats or dogs in a clever way, do it! Guaranteed engagement.
Pinterest Ads
Pinterest has recently launched its advertising campaign to allow people to spend money and promote their pins.
Because the initiative is so new, you will be asked to join the wait list before you can begin to advertise. Getting on the list is a good thing: Anything like this that's still in its infancy provides a great opportunity to strike while the iron is hot and get ahead before everyone else.
Once you join the wait list you will be asked how much you want to spend on marketing each month, but there are only two options: less than $20,000 or more than $20,000. It might seem crazy, but choose the more than $20,000 option, because Pinterest will approve your account much sooner. You don't have to spend that much but you can begin to experiment with different advertising methods to see which ones work best. Don't forget the cats.
Instagram is owned by Facebook—it's Facebook's little hipster sister! It really is geared to young, trendy people for whom their cell phones are extra limbs, so it's no surprise that it is primarily cell phone-based—the screen in Figure 7.36 is being viewed from a cell phone. Among the 300 million active monthly users, the average user uses Instagram to showcase his beautiful life; businesses are now using Instagram to display products for these users online or in-store purchases.

Figure 7.36 Instagram Post Viewed from a Cell Phone
Source: Instagram.
Engagement is sought with multiple hashtags that are relevant to your brand and those that are being searched for a lot, so it is a very good way to raise brand awareness and to build customer loyalty.
Instagram's ad format is relatively new and you will need to use the Power Editor tool to create any sort of ad. Ads follow the same structure as Facebook or Twitter sponsored posts, in that they appear on users' Instagram feed and are marked with the sponsored tag. Carousel ads are also an option—they follow the same structure as a regular sponsored post but multiple images will roll by.
Snapchat
Snapchat is aimed at a young audience, from 13- to 18-year-olds, and there are over 100 million monthly active users, which is a huge number considered how targeted the demographic is. If you are targeting people in this age cohort you should strongly consider this platform. No matter what your company or business does, every teenager grows up. By targeting members of the Snapchat generation early, they may become longer-term customers.
The unique aspect of Snapchat is that you can share a photo with somebody else and it disappears within 10 seconds or so. Now if this sounds as though advertising opportunities are extremely limited, the newly introduced My Story page has increased Snapchat's use and has made it far more accessible for brands. The My Story feature allows users to create a narrative 24 hours long by stitching together a vast range of disappearing photos and videos. It's a lot of work, but the Snapchat audience fully embraces it.
Advertising with Snapchat is currently only available for large-budget, single-day takeover ads, but it is worth taking a look at the Taco Bell account to get an idea of what can be done with Snapchat advertising. With over 200,000 friends on Snapchat and as pioneers in using “My Story” to advertise, the fast-food company know what it's doing and it does it very well.
Compared with the main cast members—Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn—social media platforms YouTube, Pinterest, Instagram and Snapchat are still supporting characters. But supporting characters often drive a story line. In the same way, deciding which platforms to utilize depends on your overall strategy and choosing a channel that is relevant to your audience.
Stage 4: Analyze
A vital aspect of running a social media campaign is to measure how it's progressing. In the same way that a sports team would never get to the top of its league without training and evaluating its game plan, a social media campaign is useless without constant analysis. You have got to flex those digital marketing muscles and to track information that will tell you what is working, what needs to be tweaked, and what should be stopped.
Analysis is stage 4 of the process, as illustrated in Figure 7.37. When you cross the finish line of this section you will:
· Know how to use the analytics features of major social media platforms to your advantage.
· Understand the importance of Google Analytics when tracking a conversion path.
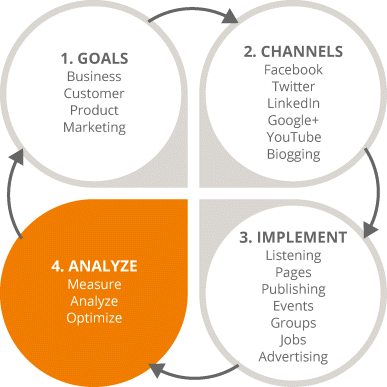
Figure 7.37 Focus on the Fourth Stage in the SMM Process
What Gets Measured, Gets Done
Each social media campaign should follow these guidelines:
1. Set measurable goals. Choose goals that are smart, specific, measurable, and attainable.
2. Track your goals. Iterate them, enhance them, and improve them over time.
3. Use analytics tools for each platform to inform your optimization and enhancement. Have your structure in place, even before you get started, so you know how you are going to measure your outcomes from the get-go.
Let's take a look at the different measurement tools available through different social media platforms.
Facebook Insights
Facebook does not want you to sit back and enjoy the returns of Facebook advertising; like any good mentor, it wants to keep its apprentices on their toes. That is why Facebook Insights continues to expand and get more elaborate every few months. Yes, it takes work, but it's worth it in the long run because of the incredible amount of useful information you can take from it. When you click into the Insights section from your Facebook page you can see seven tabs, each of which offers different pieces of information. The tabs are called Overview, Likes, Reach, Page Views, Posts, Videos, and People.
1. Overview, which is shown in Figure 7.38, reveals how many “likes” you got in the last week, how widely your post has been distributed, and what the level of engagement has been with your page.
2. Likes shows you the total page likes, how many likes your page gained and lost each day (as shown in Figure 7.39), and also shows you where your likes are coming from (as shown in Figure 7.40).
3. Reach, as shown in Figure 7.41, shows you how many people your posts have reached organically and by exactly how much your reach will increase when you spend money. This is essential for really understanding the impact of spending money on specific ads.
4. Page Views, shown in Figure 7.42, tells you how many people have visited your page and where specifically they have visited. Is it your timeline? Your photos tab? The price list? Your info tab?
5. Posts lets you know the engagement you are getting over a number of days. Take a look at the bottom of the example in Figure 7.43. Note the time frame, which runs from midnight to midnight over a 24-hour period. This is how you will know where most of your audience is based. The figure shows much less engagement from 1:00 A.M. until about 7:00 A.M., and engagement drastically increases between 6:00 A.M. and 10:00 P.M. A subtab of the Posts tab called Post Types also gives a breakdown of every single post published on your page, including the average reach of your statuses, of your photos, and of statuses with links, as well as the level of engagement.
6. Videos allows you to see overall views based on a date range you can customize, as shown in Figure 7.44. You can also switch between view breakdowns—organic versus paid, auto-played versus clicked-to-play, and unique versus repeat—by clicking on the drop-down box at the top right-hand side of the page. As shown in Figure 7.45, you can see the number of times your page's videos were viewed for 30 seconds or more. Also, in the Top Videos section of the page you can identify your page's best performing videos based on reach, views, or average completion over a desired date range.
7. People delivers a breakdown of the type of people that engaged with your posts. In Figure 7.46, you can see that 93 percent of fans are female, 7 percent are male, and 42 percent of all fans are between the ages of 25 and 34. This kind of information is critical for deciding what type of posts to publish and whom to target.
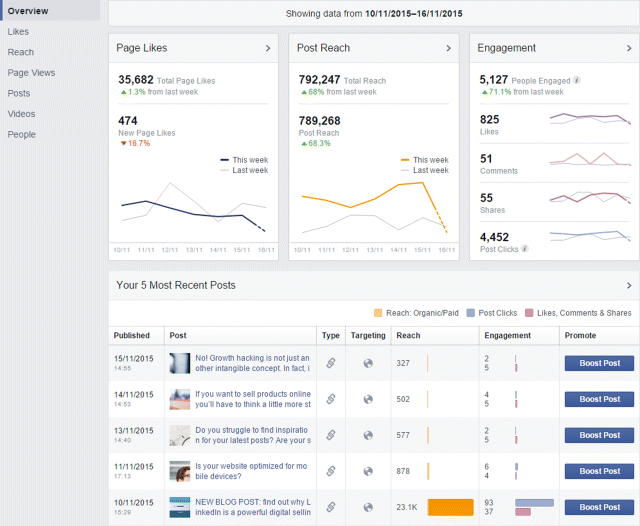
Figure 7.38 Facebook Insights Overview Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
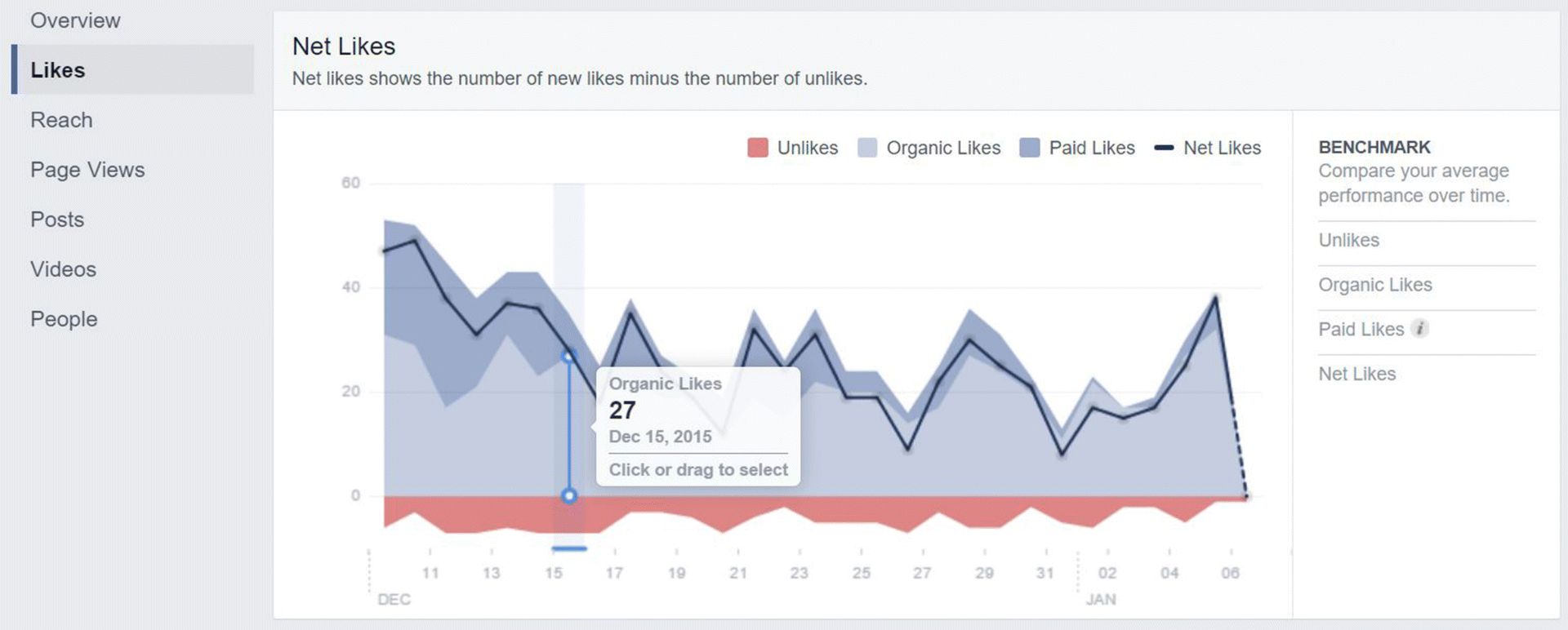
Figure 7.39 Net Likes within Facebook Insights Likes Tab
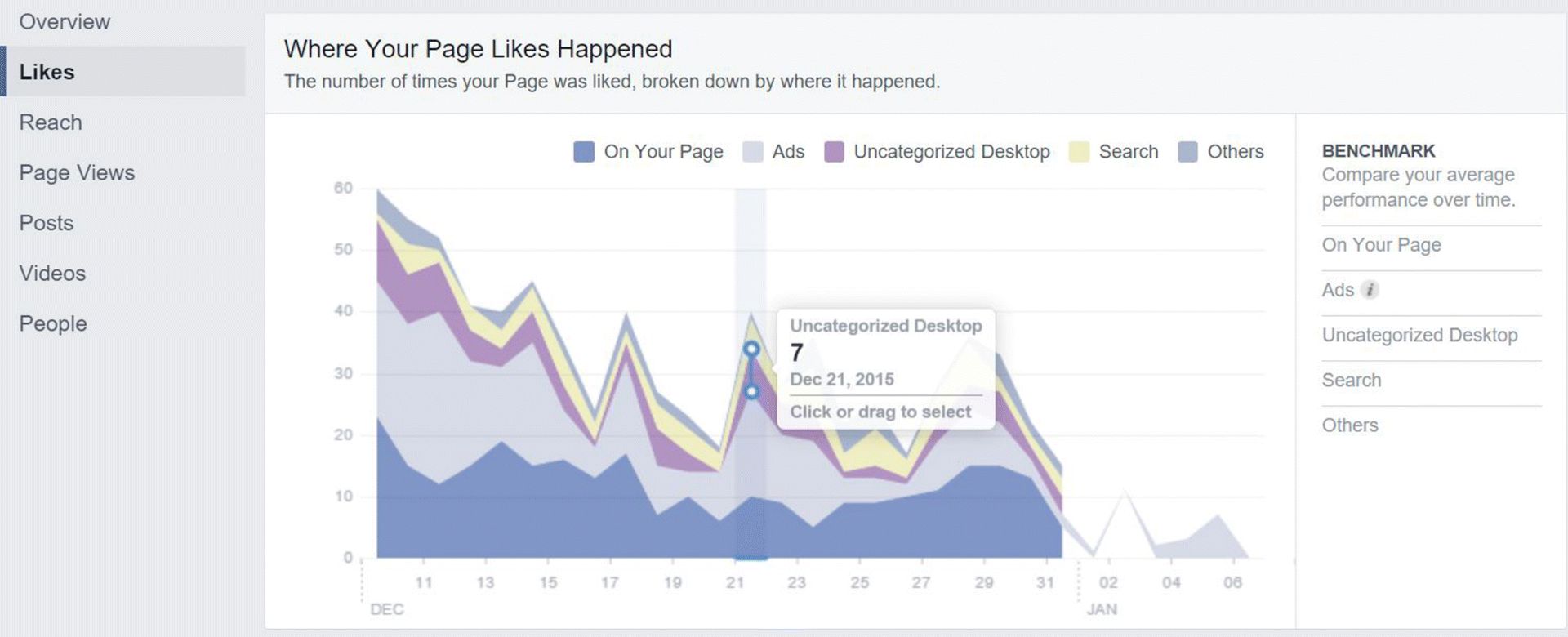
Figure 7.40 Like Attribution within Facebook Insights Likes Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
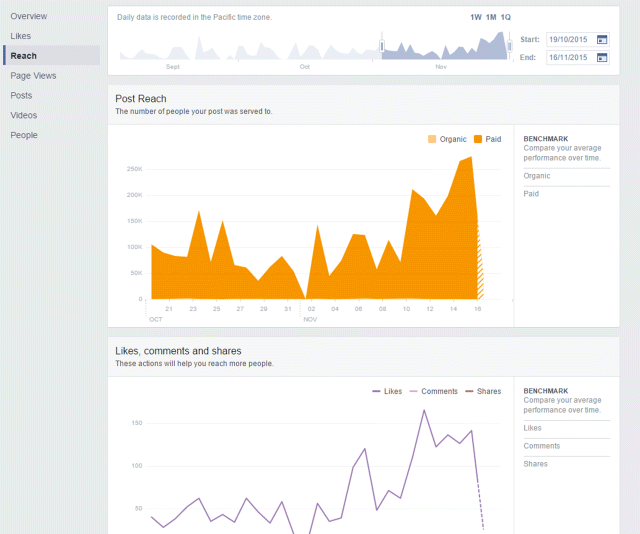
Figure 7.41 Facebook Insights Reach Tab
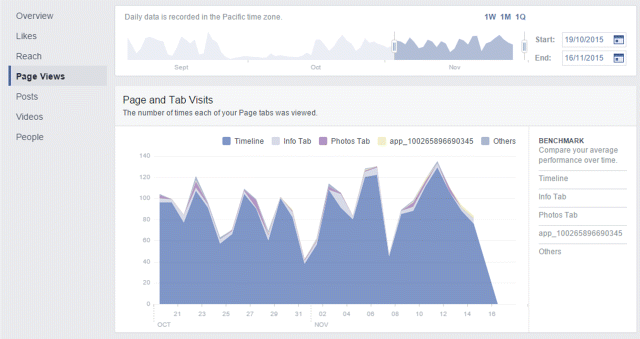
Figure 7.42 Facebook Insights Page Views Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
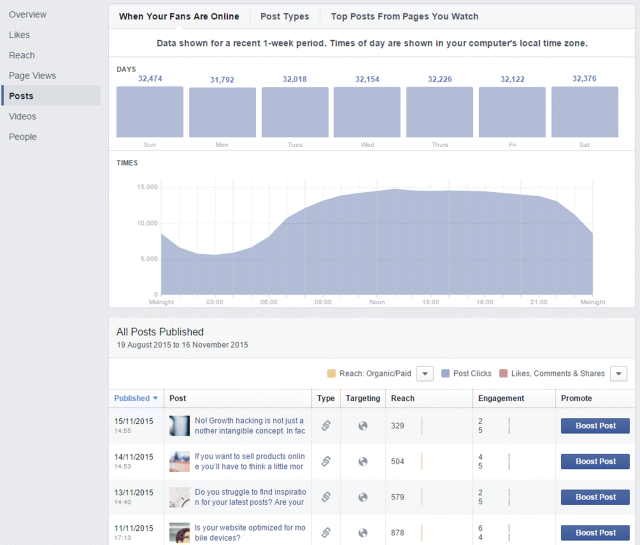
Figure 7.43 Facebook Insights Posts Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
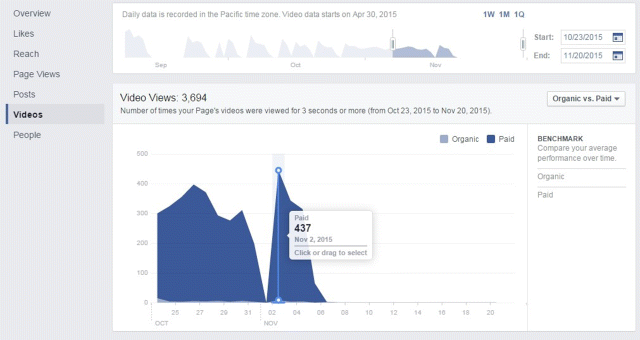
Figure 7.44 Views by Date Range within Facebook Insights Videos Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
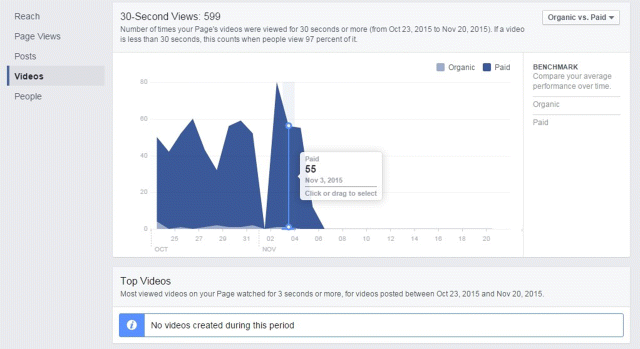
Figure 7.45 30-second View Report within Facebook Insights Video Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
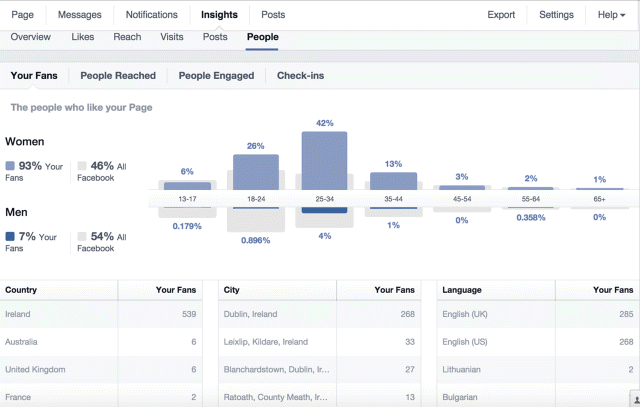
Figure 7.46 Facebook Insights People Tab
Source: Screenshot reproduced with permission of Facebook.
Yes, there is a huge mine of information to be uncovered with your virtual hammer and chisel, but just as you cannot enter a mine without a hard hat and flashlight, you must know what you are looking for before you go into Insights. Be prepared with the specific outcomes that you want from it, such as audience information and ideas on how to improve your posts and income.
Facebook Insights can measure numerous important factors including how your page is performing, if it is gaining fans and “likes,” if your posts are reaching the right people, if they are engaging with your page, and the type of content your audience prefers. If you have a Facebook page you simply must use the Insights tool. Ignore it at your peril! You may end up posting the wrong kind of content at the wrong time to the wrong audience. Could you handle the shame?
LinkedIn Analytics
While it may not be as comprehensive as Facebook Insights, LinkedIn Analytics offers valuable information on a number of different aspects of your campaign. Take a look at Figure 7.47 for an example of a company's analytics page; it gives a detailed overview of how every post is performing, the number of impressions, clicks, and interactions, as well as the percentage of engagement.
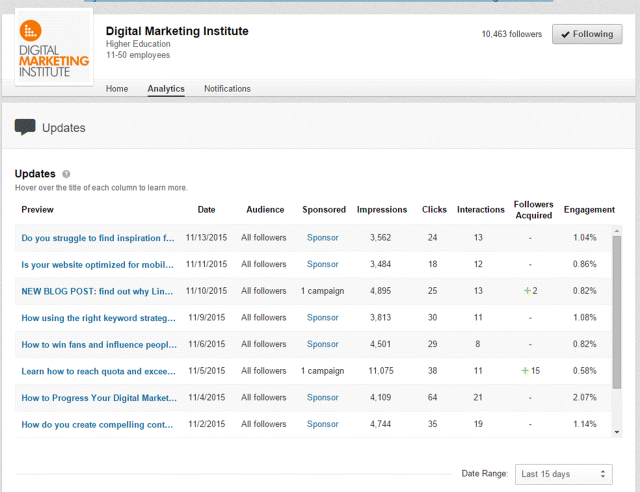
Figure 7.47 LinkedIn Analytics Overview Page
Source: LinkedIn.
If that level of insight has not satisfied your appetite for data, you can look even deeper into specific posts to see the reach (unique impressions) and engagement (clicks, “likes,” comments, shares, followers acquired, and engagement percentage), as shown in Figure 7.48.
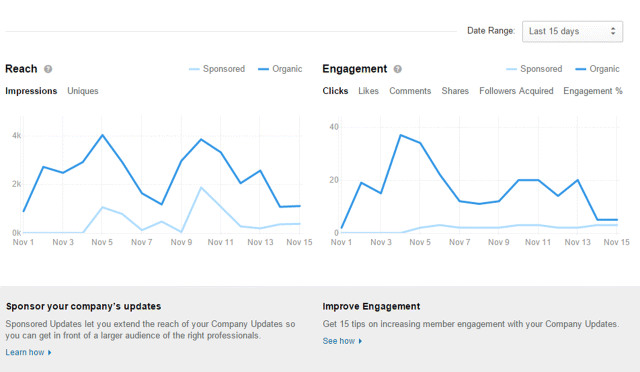
Figure 7.48 Analytics Report for Specific Post within LinkedIn
Source: LinkedIn.
As with Facebook, you can also see your audience demographics on LinkedIn, with the added bonus of being able to choose the type of demographic you are measuring. You can do this by clicking the drop-down menu on the right, which is set to Seniority in Figure 7.49. Here you can see what the level of seniority of the jobs held by your audience members is—in this example 34.2 percent are senior level, 24.9 percent entry level, 18.8 percent managers, 6.8 percent directors, and 5.5 percent owners. Other options from this audience demographic drop-down menu include company, industry type, company size, function, and employee type. A wealth of information right at your fingertips—use it!
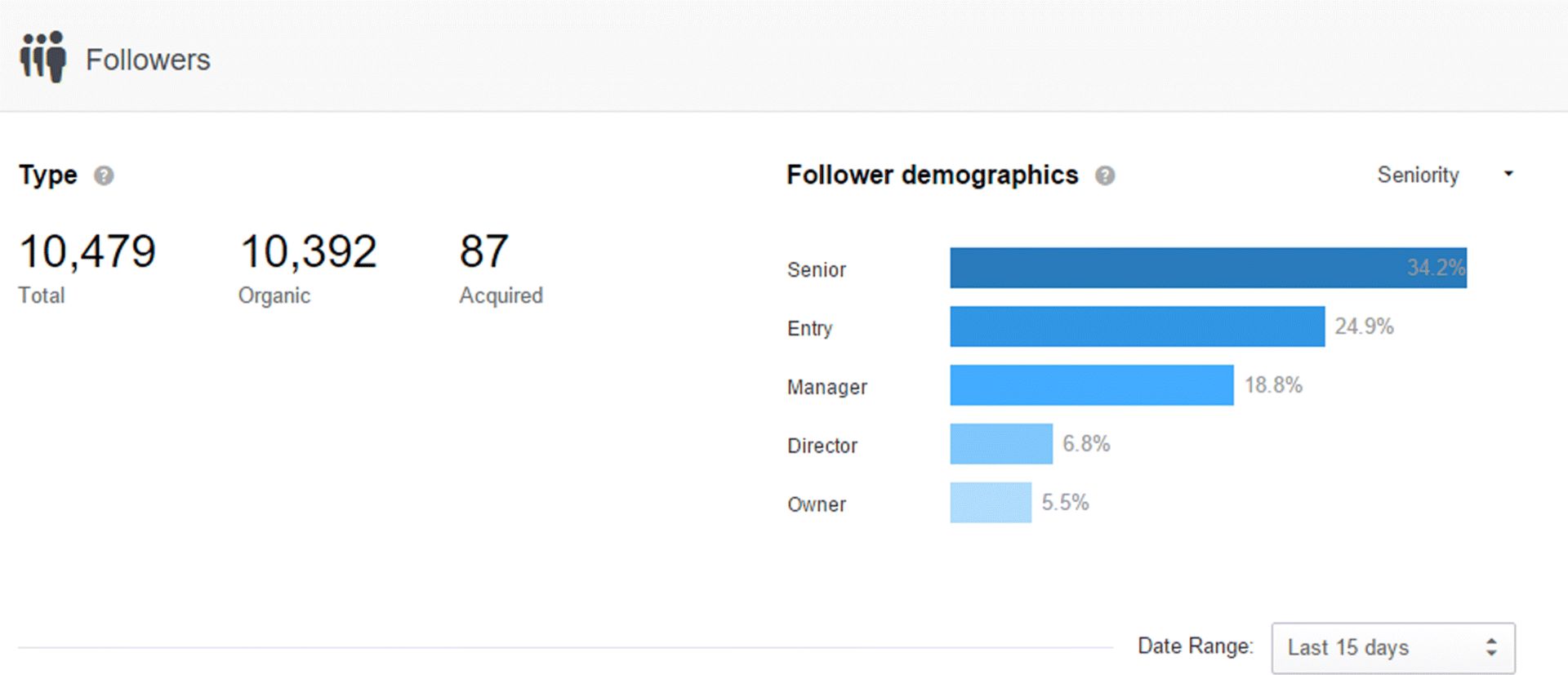
Figure 7.49 LinkedIn Demographic Drop-Down Menu
Source: LinkedIn.
You can also track your followers through LinkedIn Analytics. You can find out how many followers your company page has, if there is a trend, if your numbers are growing (as in Figure 7.50), or if they have leveled off. You should look at your followers' demographics to make sure that they are representative of your target audience. If not, your methods will need tweaking to reach the people you want to target.
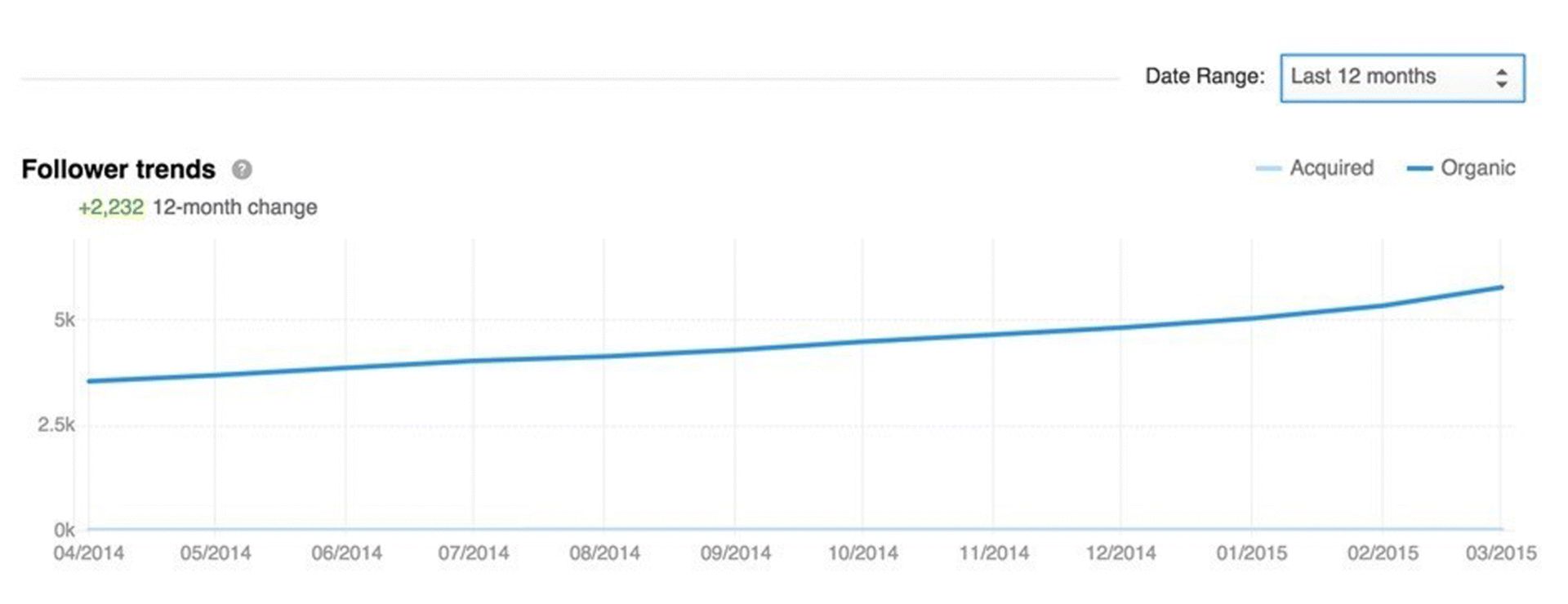
Figure 7.50 LinkedIn Follower Trends
Source: LinkedIn.
Not only that, you can measure how well you are performing against your competitors. If you provide details about your primary competitors, LinkedIn will compare your company with them in terms of the number of followers each company has, as shown in Figure 7.51.

Figure 7.51 LinkedIn Competitor Comparison
Source: LinkedIn.
The information you can gather from LinkedIn Analytics is crucial to the success of your LinkedIn page. With it, you can monitor, test, tweak, and perfect.
Twitter Analytics
The Activity Dashboard is where all Twitter monitoring happens. As you can see in Figure 7.52, it's where you track the number of tweets, impressions, profile visits, mentions, and followers that link back to your account. You can track impressions daily and see how they move up or down depending on the type of tweet you sent and whether you spent money on it or not. Use this tool to look at whether your number of followers is increasing, decreasing, or staying static, and figure out why.
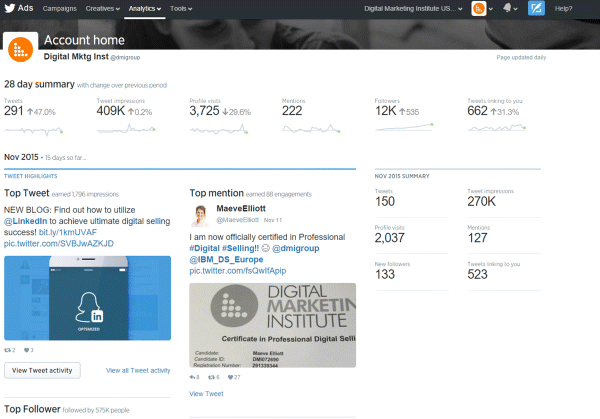
Figure 7.52 Twitter Analytics Tweet Activity Dashboard
Source: Twitter.
Twitter Analytics lets you see if your followers' demographics are representative of your target audience. It also tells you what content types your audience members prefer, whether that is a standard tweet or a tweet with photos, videos, or links. Detailed analysis on engagement in the form of tweets, retweets, replies, favorites, and link clicks are easily obtainable. You can even see both what time of day your followers are most active and the times that deliver the best impressions for your tweets.
Google+ Insights
While Google+ is the serious older brother in the social media family, it is an advantageous channel to utilize if you have a local business or a business that is physical in any form. Your ranking on Google Search and Google Maps depends on it.
The function of Google+ Insights is to keep an eye on:
· Visibility. How many views you are getting (shown in Figure 7.53)?
· Engagement. How many actions of engagement have taken place over the past 30 days (shown in Figure 7.54)?
· Audience. How many new followers have you got and where are they coming from (shown in Figure 7.55)?
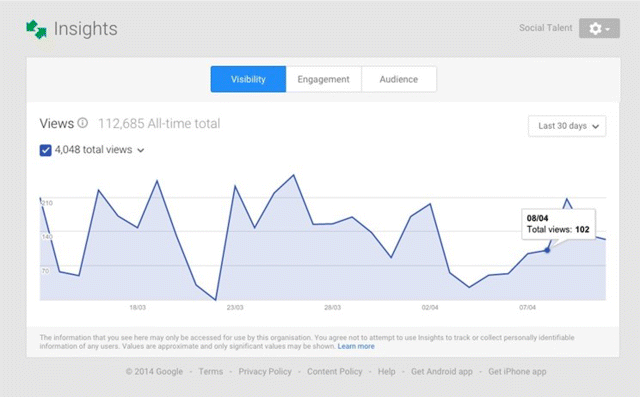
Figure 7.53 Visibility Tab of Google+ Insights
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
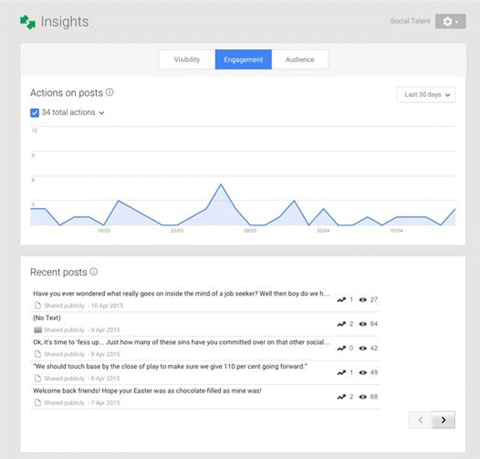
Figure 7.54 Engagement Tab of Google+ Insights
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
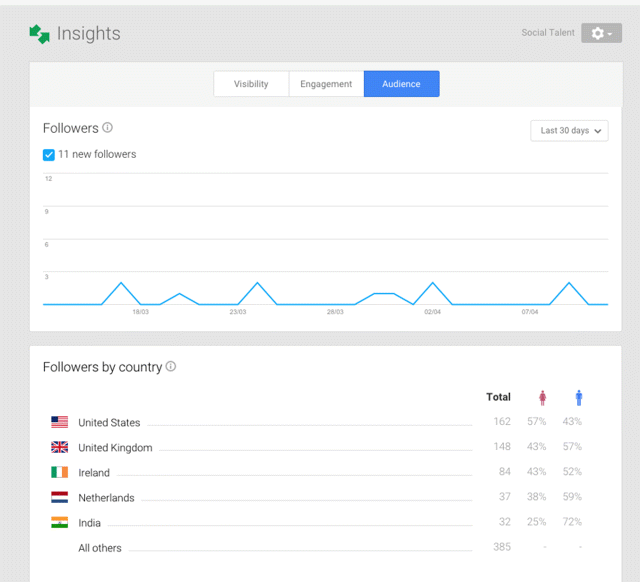
Figure 7.55 Audience Tab of Google + Insights
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
In the example shown in Figure 7.55, most followers come from the United States, and 57 percent of those are female and 43 percent male.
The types of metrics available in Google Plus are very similar to the other social media platforms. You can see how your Google+ followers are growing over time, if the demographics of your followers are representative of your target audience, how your posts are performing, and which types of posts your audience prefers. After determining that information, you can then look at how your Google+ audience members behave when they land on your website and what the conversion rate is.
YouTube Analytics
You can gain a plethora of really useful information from YouTube, thanks to its association with Google AdWords. The dashboard gives you tabs for data overview as well as reports on real time, earnings, estimated earnings, ad performance, demographics, playback locations, traffic sources, devices, audience retention, engagement reports, subscribers, likes, dislikes and favorites. The list is exhaustive and can appear overwhelming at first. But once you are familiar with how it works, you can pluck a wealth of information left, right, and center! To navigate YouTube Analytics, work your way down the menu on the left and go through each section one by one.
Just by glancing at the demographics section, as shown in Figure 7.56, you can see your followers' gender, location, age group, and number of views. Unless you know exactly what to look for, you can become lost in YouTube Analytics, so plan ahead before you start trawling through it.
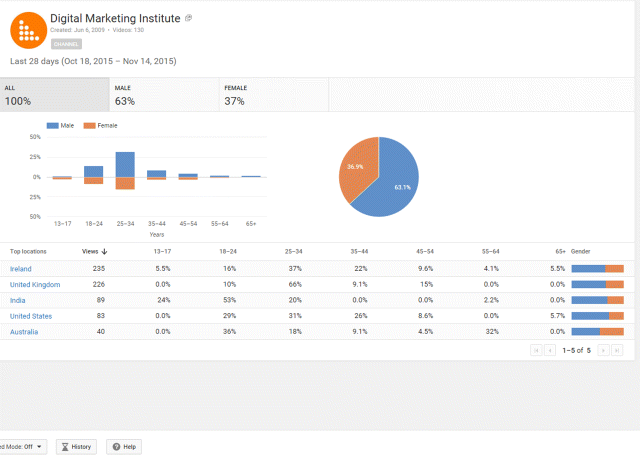
Figure 7.56 Demographics Section of Youtube Analytics
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
Google Analytics
Social media platform analytics are nothing in comparison to Google Analytics, the queen of all things data. It allows you to measure traffic sources, and from that, figure out the top conversion path. The bottom line is, you have to know where your visitors are coming from to get more leads and generate more income for your business.
Let's take a look at Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter on Google Analytics to get a better idea of how you can track a conversion path.
Take note of the specific visits from Facebook and the number of people who then converted into a specific action from Figure 7.57. This is hugely beneficial information, as when you know how to use Analytics you can give those people a conversion value. For example, if you give each lead generated a value of $10, and 94 of these gave their email addresses, the total conversion value is $940. If you could take out 173 conversions, based on the value assigned, that gives them a $940 conversion value.
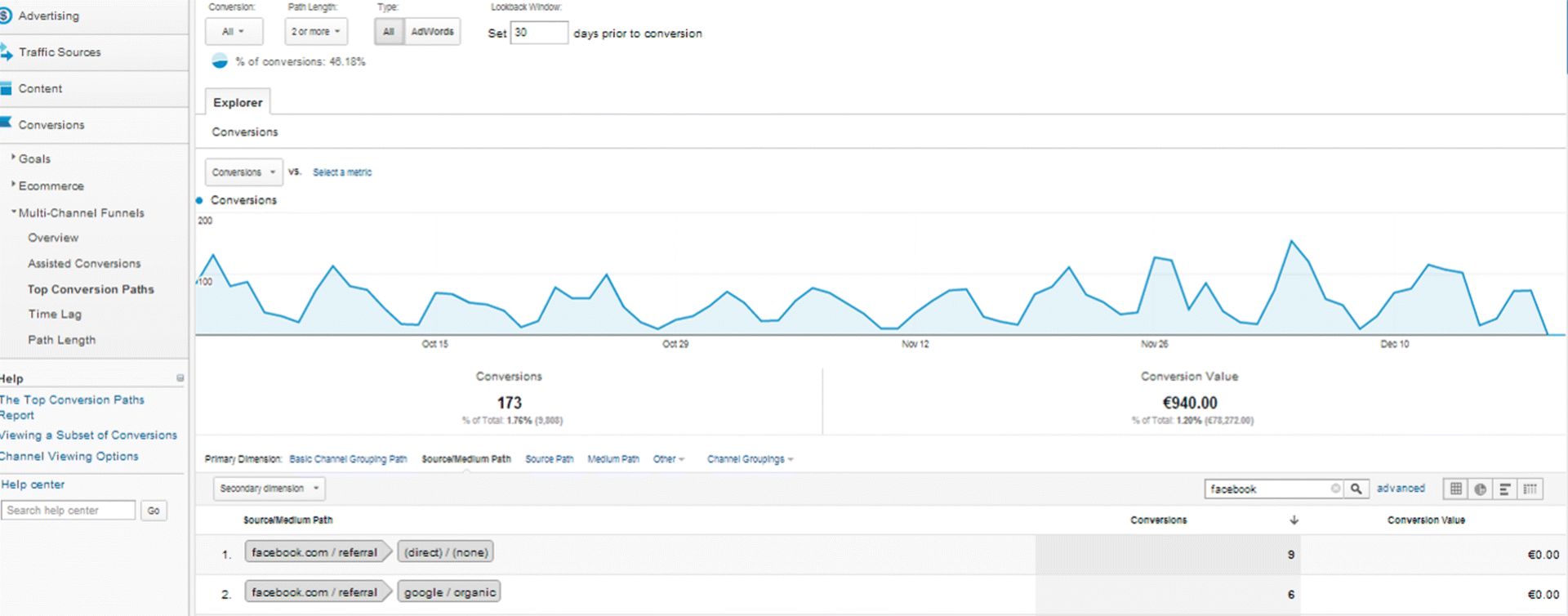
Figure 7.57 GA Facebook Conversions
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
Looking at Figure 7.58 and the same 173 conversions on LinkedIn, you will see that the total conversion was approximately 50 percent on top of that, amounting to $1,535.
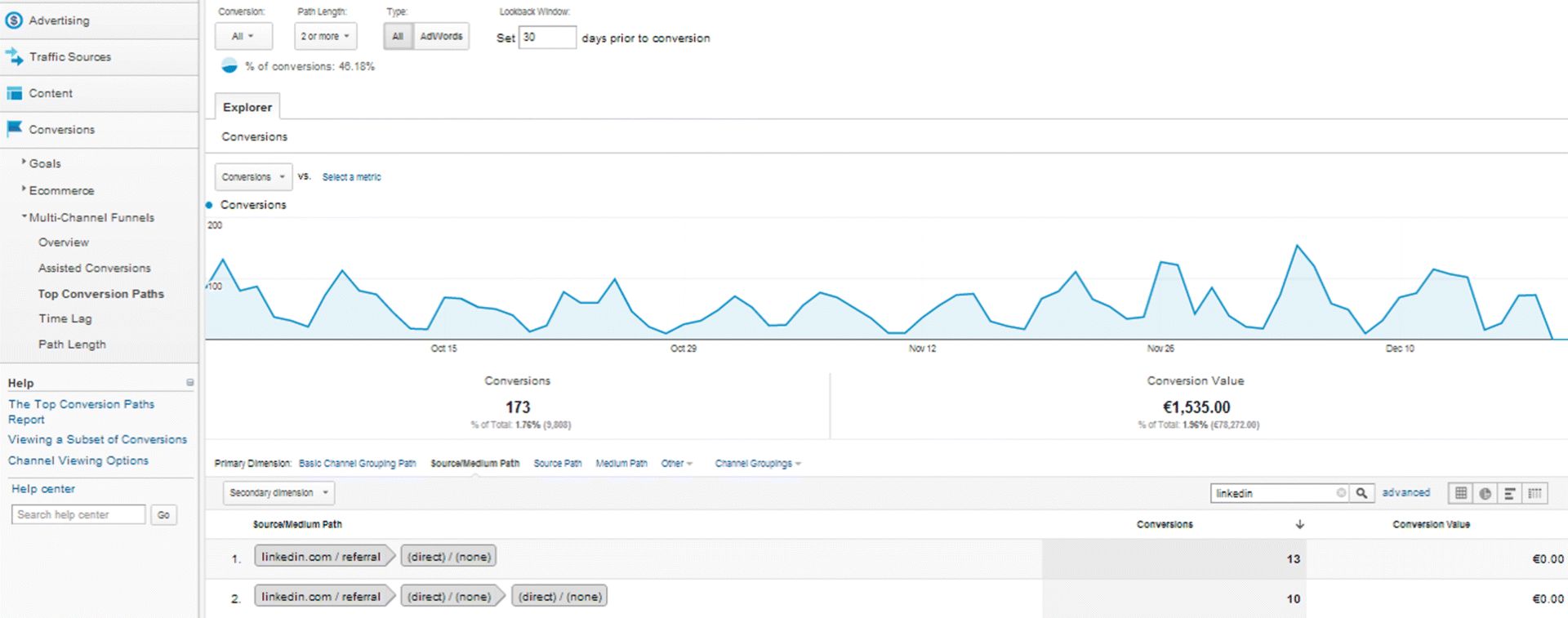
Figure 7.58 GA LinkedIn Conversions
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
While Facebook and LinkedIn were clearly successful, Figure 7.59 shows that Twitter only has 40 conversions with a total conversion value of $50.
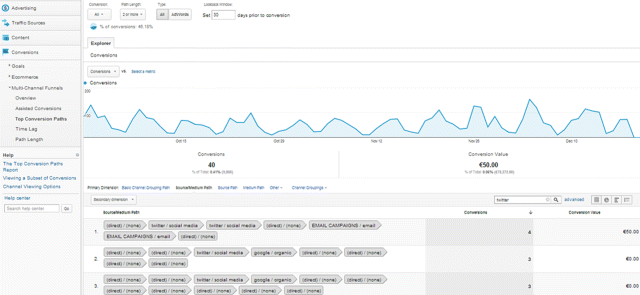
Figure 7.59 GA Twitter Conversions
Source: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google Inc.; used with permission.
Once you check what the total spend was, Google Analytics can tell you what the specific goal flow is. From this, you can see where the source of the traffic is, how many of those people went on to the Contact Us page, and how many of those people went further again and took a specific action.
Social Media KPIs
Using the chart in Figure 7.60 is a good way of tracking overall performance and the KPI for each objective. Before you start along your social media adventures, you should know what KPIs to keep track of. Successful SMM is an iterative process that involves tracking and optimizing all aspects of your activities.
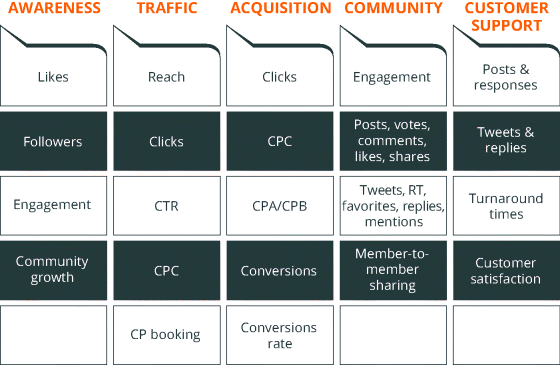
Figure 7.60 GA Twitter Conversions
Neglecting to monitor your social media journey is like going for a walk while it's snowing and expecting to follow your footsteps back. No good will come of that! So, as you are setting up your overall strategy and planning your advertising campaign, make sure to set up a measurement system. The process of iteration allows you to maximize the effectiveness and ROI of your activities over time, helping you to ultimately achieve your business goals.
Laws and Guidelines
The clock is striking 12 on social media part 2's iterative journey, but before we prepare to start the cycle all over again, let's take time to learn some important information on laws concerning social media.
When you complete this section you will:
· Be aware that certain laws apply to all social networks.
· Understand the only way to have complete control of the data about your consumers is via a forum other than social media.
Data Protection and Privacy
Social media is an international game, so along with being up to speed on the laws in your own country you must also be aware of laws worldwide. There is no need to visit your local law library—there are various websites to help you with this, such as www.dlapiperdataprotection.com.
Do some research on data protection laws so that you know the rules that cover collecting people's data. For instance, you can only use personal data in certain ways, and you must dispose of it after a certain number of years. It is very important to remember that you can only use this kind of information for the purposes for which you collected it.
Copyright Issues
Copyright becomes more relevant when you are using websites like Pinterest and Instagram. If you are just randomly sharing people's photographs or images, be aware of what you can do and what you can't do when it comes to copyrighted images.
Organizational Policy Documents
Despite being able to freely gather information, you do not own any of these social media pages. They are the property of the company that owns the social network, such as Facebook and Twitter. Have a back-up strategy in place so that you can own as much data about your consumers as you can. Get as many people as possible off social media and into a forum that you can manage and that you have 100 percent ownership of, like an email directory database.
Social media is the New York City of the Internet—it never, ever sleeps. You have the power to keep up with the best of them by using all of the features and tools available to each platform. But be mindful that if you do not obey the guidelines that are put forth for a reason, you run the risk of your social media plan being stopped in its tracks.
So, What Have You Learned in This Chapter?
Go forth, social butterfly, and delight the masses with your engaging content across the plethora of platforms available to you. And if you are ever in need of another social media revamp, just remember:
· It's a team effort—assign members with different strengths to your SMM team and consider up-skilling if necessary.
· Listen to your customers and prove it by being reactive.
· Schedule your content—don't overwhelm your audience!
· Focus on quality rather than quantity when it comes to your social media interactions.
· Social platforms are constantly evolving—keep up-to-date and ahead of the game!

Go to www.artofdmi.com to access the case study on SMM as additional support material for this chapter.
 Exercises
Exercises
Exercise 1
You are a new 24-hour gym opening in Manhattan and your main target market is working professionals (ages 25 to 40) who either live in the area or are visiting for business. Corporate packages are a new venture for the gym.
Create a content schedule for your Facebook page for the next seven days. Consider the type of posts that would be interesting and engaging to your potential customers.
Note: There must be a split overall into 70 percent your own content, 20 percent shared content, and 10 percent or less selling.
Exercise 2
Log into your business page on Facebook and go to https://www.facebook.com/ads/audience_insights. Create an audience based on your gym's target market and examine the data. What does the data tell you about your audience in regards to:
· Gender split
· Age profile
· Relationship status
· Job titles
· Interests
Exercise 3
Under Manage Ads in LinkedIn, click on Create a New Campaign and create an ad that will draw people to your website. Name your campaign, choose your ad text, and upload an image. Now set up a second variant so you can split test different wording, images, or both and preview your ad. Then choose a target market for your gym based on the criteria above. (Remember you also want to target corporate clients in the area.) Choose your budget.
Exercise 4
As of tomorrow, you will be waiving your gym join-up fee for the entire month. Go to Twitter Ads and create a new followers campaign. Customize the start and end dates and compose a new tweet for your ad—remember to include the benefits and a CTA.
· Select your targeted audience.
· Add targeted followers.
· Add by interest.
· Choose your budget.
Exercise 5
If you don't already have an Instagram account, download the app and set one up. Then visit http://iconosquare.com and click Sign In with Instagram.
Click on Analytics and export your analysis report for the month.
Record the following:
· Number of “likes”
· Your most liked images for the month
· Your engagement scores
· Follower growth
· Your 10 most engaged followers
Use the information to shape your Instagram activity and compare it with your next monthly report.
 Action Plan: SMM
Action Plan: SMM
Digital Marketing Planning Scheme for SMM
Objectives
Reach, engagement, advocacy, conversion
Action Items
· Content creating (blog posts, ebooks, white papers, infographics, GIFs, video)
· Social posting (created content, curated content, images, video, links, offers)
· Engaging (CTAs, comments, questions, polls, surveys)
· Promoting (promoted social posts, ads, competitions, product promotions, events)
· Community building (conversation, customer service, comments, suggestions)
Measurement Tools and KPIs
Social media insights and analytics: Shares, comments, clicks, goals, social referral traffic to website, site content traffic, conversions
Spend
|
Media |
Content |
People |
Systems |
|
x |
X |
x |
x |